Cisco 7925G Administration Guide - Page 31
Overview of the VoIP Wireless Network, Understanding the Wireless LAN
 |
UPC - 882658201943
View all Cisco 7925G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 31 highlights
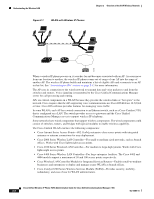
2 C H A P T E R Overview of the VoIP Wireless Network This chapter provides an overview of the interaction between the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G and other key components of a VoIP network in a wireless local area network (WLAN) environment. It contains the following sections: • Understanding the Wireless LAN, page 2-1 • Understanding WLAN Standards and Technologies, page 2-3 • Bluetooth Wireless Technology, page 2-8 • Components of the VoIP Wireless Network, page 2-9 • Security for Voice Communications in WLANs, page 2-16 • VoIP WLAN Configuration, page 2-21 • Site Survey Verification, page 2-22 Understanding the Wireless LAN With the introduction of wireless communication, wireless IP phones can provide voice communication within the corporate WLAN. The Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G depends upon and interacts with wireless access points (APs) and key Cisco IP telephony components, including Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, to provide wireless voice communication. In a traditional LAN, IP phones and computers use cables to transmit messages and data packets. Cisco Unified WLAN delivers security, scalability, reliability, ease of deployment, and management similar to wired LANs. It includes RF capabilities that enable real-time access to core business applications and provides proven enterprise-class secure connectivity. The WLAN is an integrated end-to-end solution that uses wireless IP phones and APs, network infrastructure, network management, and mobility services. Figure 2-1 shows a typical WLAN topology that enables the wireless transmission of voice for wireless IP telephony. OL-15984-01 Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager 7.0(1) 2-1