ZyXEL NBG6515 User Guide - Page 63
Overview, What You Can Do, What You Need to Know
 |
View all ZyXEL NBG6515 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 63 highlights
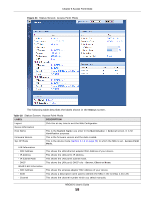
CHAPTER 9 Universal Repeater Mode 9.1 Overview In universal repeater mode, your NBG can act as an access point and wireless client at the same time. The NBG can connect to an existing network through another access point and also lets wireless clients connect to the network through it. This helps you expand wireless coverage when you have an access point or wireless router already in your network. In the example below, the NBG (A) is configured as a universal repeater. It has three clients that want to connect to the Internet. The NBG wirelessly connects to the available access point (B). Figure 46 Universal Repeater Mode B A After the NBG and the access point connect, the NBG acquires its IP address from the access point. The clients of the NBG can now surf the Internet. 9.2 What You Can Do • Use the Status screen to view read-only information about your NBG (Section 9.5 on page 64). • Use the AP Select screen to choose an access point that you want the NBG to connect to. You should know the security settings of the target AP (Section 9.6 on page 67). • Use other Wireless LAN screens to configure the wireless settings and wireless security between the wireless clients and the NBG. • Use the LAN screen to set the IP address for your NBG acting as an access point (Section 8.5 on page 60). 9.3 What You Need to Know With the exception of the Network > Wireless LAN 2.4G/5G > AP Select screens, other configuration screens in Universal Repeater Mode are similar to the ones in Access Point Mode. NBG6515 User's Guide 63