Cisco 7920 Administration Guide - Page 36
The 802.11 Standards for Wireless LAN Communications - series
 |
UPC - 746320774732
View all Cisco 7920 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 36 highlights
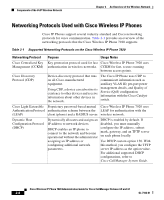
Understanding the Wireless LAN Chapter 2 An Overview of the Wireless Network WLANs require access point devices that receive and transmit radio signals. Cisco Aironet Access Points, such as the 1200, 1100, and 350 series models, support voice on a WLAN. Figure 2-1 shows a typical WLAN topology that incorporates wireless data for laptop computers and wireless IP telephony (WIPT) for Cisco Wireless IP Phone 7920 models. When a wireless device powers on, it immediately searches for and becomes associated with an access point. As users move from one location to another within the corporate WLAN environment, the wireless device roams out of range of one access point and into the range of another. The access point uses the wired network to transmit data and voice packets to the switches and routers. Voice packets are sent to the Cisco CallManager server for call processing and routing. Figure 2-1 Wireless LAN with Cisco Wireless IP Phone 7920s 113946 M The 802.11 Standards for Wireless LAN Communications Wireless LANs must follow the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) 802.11 standards that define the protocols that govern all Ethernet-based wireless traffic. The 802.11b standard is the most prevalent standard in wireless Cisco Wireless IP Phone 7920 Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager Release 4.0 and 4.1 2-2 OL-7104-01