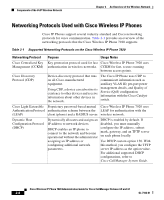
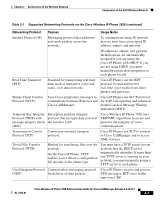
Cisco 7920 Administration Guide - Page 45
With the release of the Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Wireless LAN Services, Module WLSM - modulator
 |
UPC - 746320774732
View all Cisco 7920 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 45 highlights
Chapter 2 An Overview of the Wireless Network Components of the VoIP Wireless Network points are in the same Layer 2 subnet, the Cisco Wireless IP Phone keeps the same IP address and the call continues. As a Cisco Wireless IP Phone roams between access points, it must re-authenticate with each new access point. See the "Security Mechanisms in the Wireless Network" section on page 2-13 for information about authentication. If the Cisco Wireless IP Phone user moves from an access point that covers IP Subnet A to an access point that covers IP Subnet B, the phone no longer has an IP address or gateway that is valid within the new subnet and the call can disconnect. With the release of the Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Wireless LAN Services Module (WLSM), the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 7920 now supports Layer 3 roaming. For details about the Cisco WLSM, refer to the product documentation available at: http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/lan/cat6000/cfgnotes/wls m_1_1/index.htm • Fast and Secure Roaming-Cisco Centralized Key Management (CCKM) enables authenticated client devices to roam securely from one access point to another without any perceptible delay during reassociation. With the support of CCKM protocol, the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 7920 is able to negotiate the handoff from one access point to another more easily. During the roaming process, the phone must scan for the nearby access points, determine which access point can provide the best service, then reassociate with the new access point. When implementing stronger authentication methods, such as WPA and LEAP, the number of information exchanges increases and causes more delay during roaming. For details about CCKM, refer to the "Cisco Fast Secure Roaming Application Note" at: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/wireless/ps4570/prod_technical_r eference09186a00801c5223.html To solve this issue, CCKM, a centralized key management protocol, provides a cache of session credentials on the wireless domain server (WDS). As the phone roams from one access point to the next, CCKM compresses the number of message exchanges during roaming by providing a master key stored on the WDS for the access point to use. The reassociation exchange is reduced to two messages, thereby reducing the roaming time. Related Topics • Voice Quality in a Wireless Network, page 2-12 OL-7104-01 Cisco Wireless IP Phone 7920 Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager Release 4.0 and 4.1 2-11