Cisco 7920 Administration Guide - Page 37
Connecting to the Wireless Network - technologies
 |
UPC - 746320774732
View all Cisco 7920 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 37 highlights
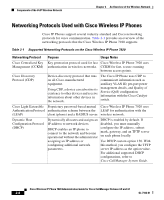
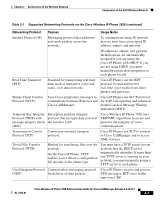
Chapter 2 An Overview of the Wireless Network Understanding the Wireless LAN LAN communications and is commonly called WiFi. The 802.11b standard specifies the radio frequency (RF) of 2.4 GHz for both transmitting and receiving data at speeds of 1, 2, 5.5 and 11 Mbps. The 2.4 GHz RF range is an open frequency range that does not require licensing. Many devices operate in this bandwidth including cordless phones and microwave ovens; consequently, wireless communication is susceptible to interference or noise. Interference does not destroy the signal, but can impede the transmission speed and reduce an 11 Mbps signal all the way down to a 1Mbps signal. In addition, RF interference can reduce the voice quality over the wireless network. To help prevent interference, direct-sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) technology was developed to spread the signal out over the frequency range or bandwidth. DSSS technology multiplexes chunks of data over several frequencies so that multiple devices can communicate without interference. Each device has a special code that it uses to identify its data packets and to ignore all others. The Cisco wireless products use DSSS technology to support multiple devices on the WLAN. Connecting to the Wireless Network The critical components in the wireless network are the access points that provide the wireless links (or "hot spots") to the network. Cisco requires that the access points supporting voice communications must run Cisco IOS Version 12.2(15)JA or later. Cisco IOS provides features for managing voice traffic. The Cisco Aironet Access Points that support IOS include the following access point series: • Cisco Aironet Access Point 350 • Cisco Aironet Access Point 1100 • Cisco Aironet Access Point 1200 Each access point has a hard-wired connection to a network layer switch, such as a Cisco Catalyst 4000, that is configured on the LAN. The switch provides access to gateways and the Cisco CallManager server to support wireless IP telephony (WIPT). Access points transmit and receive RF signals over channels within the 2.4 GHz frequency band. Regulatory domains determine the number of channels that wireless communications can use within the 2.4 GHz frequency band. The Cisco Aironet Access Points support up to 11 communication channels in North America, 13 channels in Europe (ETSI) and 14 channels in Japan. An access point Cisco Wireless IP Phone 7920 Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager Release 4.0 and 4.1 OL-7104-01 2-3