Cisco 7920 Administration Guide - Page 38
Securing Voice Communications - wpa configuration
 |
UPC - 746320774732
View all Cisco 7920 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 38 highlights
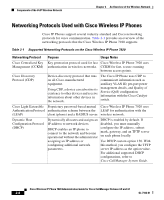
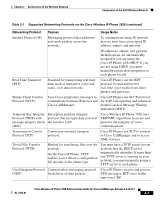
Understanding the Wireless LAN Chapter 2 An Overview of the Wireless Network broadcasts on a specific channel within the available channel range. To provide a stable wireless environment and reduce channel interference, you must specify non-overlapping channels for each access point. The recommended channels are 1, 6, and 11 in North America. The access point has a transmission range or coverage area that depends on its type of antenna and transmission power. The access point coverage range is from 500 to 1000 feet with effective isotropic radiated power (EIRP) output that scales at 1, 5, 20, 50, and 100mW. To provide effective coverage, access points need a range overlap of approximately 20 percent to allow uninterrupted connections as phone users roam from one access point to another. Wireless network devices use a service set identifier (SSID). The SSID provides a way to group a set of user devices that can associate with a set of access points. Each wireless device that can use the access point is configured with the same SSID as the access point. For more information about configuring the access points, refer to the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 7920 Design and Deployment Guide. Securing Voice Communications Because all WLAN devices that are within range can receive all other wireless LAN traffic, securing voice communications is critical. To ensure that voice traffic is not manipulated or intercepted by intruders, the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 7920 and Cisco Aironet Access Points are supported in the overall Cisco SAFE Security architecture. To secure voice communications, wireless networks use authentication and encryption methods. Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) is the method that was first introduced for wireless security, but this method is easily compromised. To address the security problems and weaknesses of WEP, the WiFi Alliance defined Wireless Protected Access (WPA.) Wi-Fi Protected Access is a standards-based, interoperable security enhancement that increases the level of data protection and access control for existing and future wireless LAN systems. It is derived from and will be forward-compatible with the upcoming IEEE 802.11i standard. WPA leverages Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) for data protection and 802.1X for authenticated key management. Cisco Wireless IP Phone 7920 Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager Release 4.0 and 4.1 2-4 OL-7104-01