HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Network Management and Mon - Page 113
Configuration prerequisites, The source sends packets to the destination port at regular intervals.
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 113 highlights
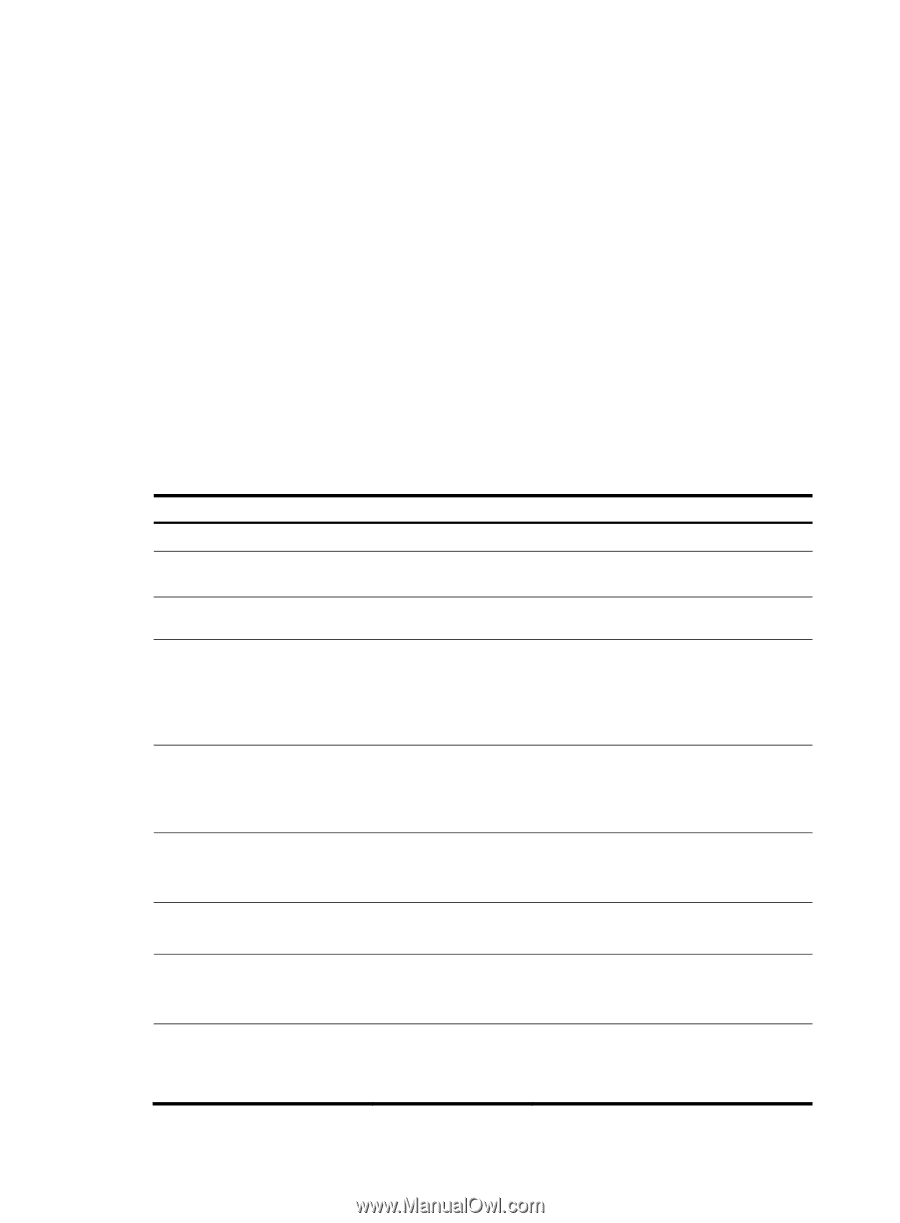
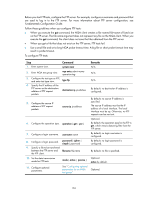
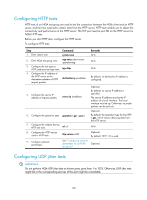
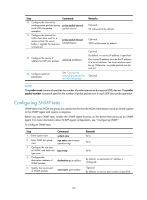
Real-time services such as voice and video have high requirements on delay jitters. UDP jitter tests of an NQA test group obtain uni/bi-directional delay jitters. The test results help you verify whether a network can carry real-time services. A UDP jitter test performs the following procedure: 1. The source sends packets to the destination port at regular intervals. 2. The destination affixes a time stamp to each packet that it receives, and then sends the packet back to the source. 3. Upon receiving the response, the source calculates the delay jitter, which reflects network performance. Delay refers to the amount of time it takes a packet to be transmitted from source to destination or from destination to source. Delay jitter is the delay variation over time. Configuration prerequisites UDP jitter tests require cooperation between the NQA server and the NQA client. Before you start UDP jitter tests, configure UDP listening services on the NQA server. For more information about UDP listening service configuration, see "Configuring the NQA server." Configuration procedure To configure UDP jitter tests: Step 1. Enter system view. Command system-view Remarks N/A 2. Enter NQA test group view. nqa entry admin-name operation-tag 3. Configure the test type as UDP jitter, and enter test type view. type udp-jitter N/A N/A 4. Configure the destination address of UDP packets. destination ip ip-address By default, no destination IP address is configured. The destination IP address must be the same as that of the listening service on the NQA server. 5. Configure the destination port destination port of UDP packets. port-number By default, no destination port number is configured. The destination port must be the same as that of the listening service on the NQA server. 6. Specify the source port number of UDP packets. source port port-number Optional. By default, no source port number is specified. 7. Configure the size of the data field in each UDP packet. data-size size Optional. 100 bytes by default. 8. Configure the string to be filled in the data field of each data-fill string probe packet. 9. Configure the number of probe packets to be sent probe packet-number during each UDP jitter probe packet-number operation. Optional. By default, the string is the hexadecimal number 00010203040506070809. Optional. 10 by default. 106