HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Network Management and Mon - Page 85
Layer 2-LAN Switch Command Reference, Layer 2 remote port mirroring implementation - switch commands
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 85 highlights
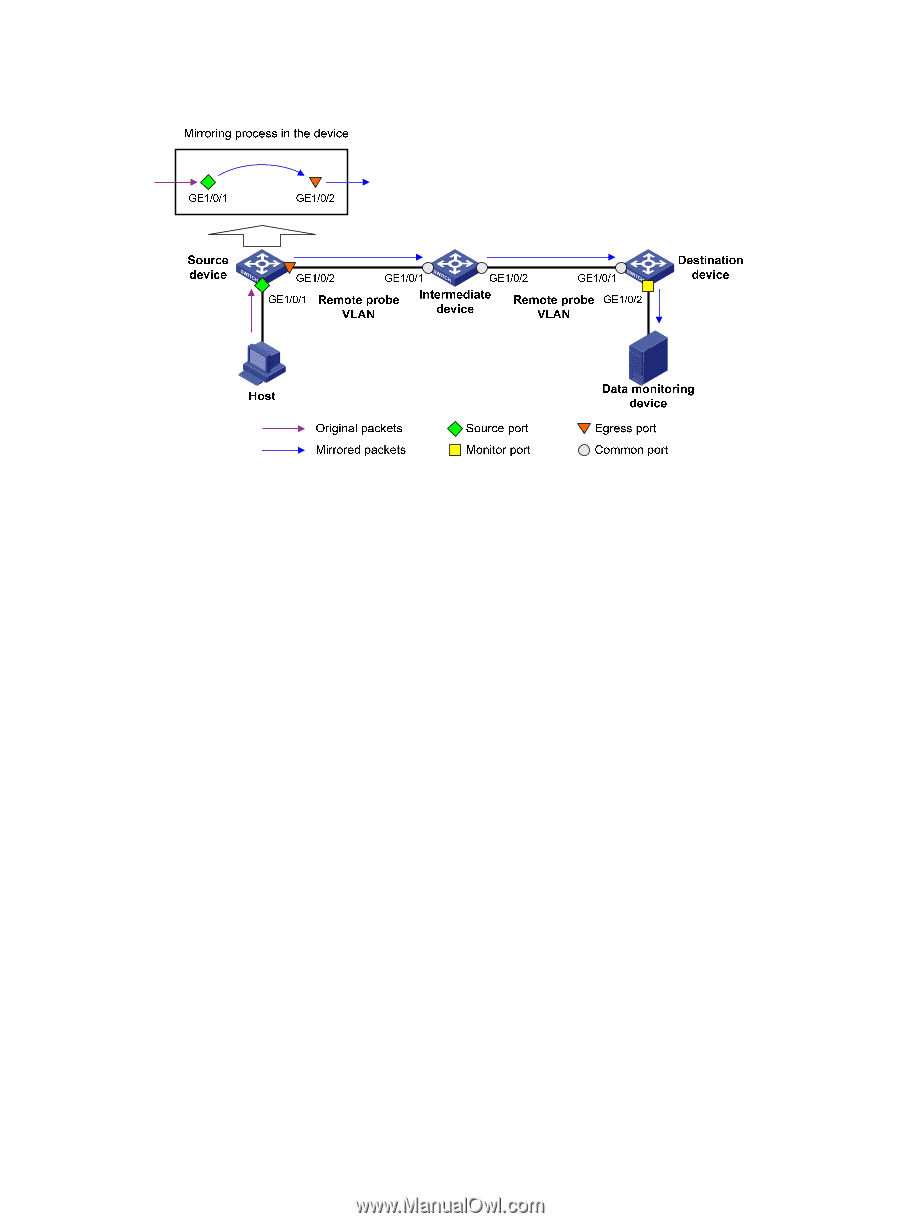
Figure 32 Layer 2 remote port mirroring implementation On the network shown in Figure 32, The source device does the following: 1. Copies the packets received on the source port GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 to the egress port GigabitEthernet 1/0/2. 2. Forwards the packets to the intermediate device, which then broadcasts the packets in the remote probe VLAN. 3. Transmits the packets to the destination device via the intermediate device. Then, the destination device does the following: 4. Receives the mirrored packets. 5. Compares their VLAN IDs to the ID of the remote probe VLAN configured in the remote destination group. 6. If the VLAN IDs of these mirrored packets match the remote probe VLAN ID, the device forwards them to the data monitoring device through the monitor port GigabitEthernet 1/0/2. Allow remote probe VLAN to pass through the intermediate devices to make sure the source device and the destination device can communicate at Layer 2 in the remote probe VLAN. For a mirrored packet to successfully arrive at the remote destination device, make sure the VLAN ID of the mirrored packet is not removed or changed. Otherwise, the Layer 2 remote port mirroring configuration will fail. To monitor both the received and sent packets of a port in a mirroring group, you must use the mac-address mac-learning disable command on the source, intermediate, and destination devices to disable MAC address learning of the remote probe VLAN. For more information about the mac-address mac-learning disable command, see Layer 2-LAN Switch Command Reference. 78