HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Network Management and Mon - Page 60
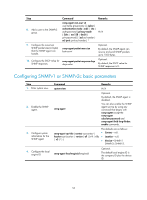
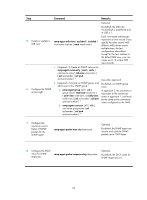
SNMP operations, SNMP protocol versions, SNMP configuration task list
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 60 highlights
A MIB view represents a set of MIB objects (or MIB object hierarchies) with certain access privilege and is identified by a view name. The MIB objects included in the MIB view are accessible while those excluded from the MIB view are inaccessible. A MIB view can have multiple view records each identified by a view-name oid-tree pair. You control access to the MIB by assigning MIB views to SNMP groups or communities. SNMP operations SNMP provides the following basic operations: • Get-The NMS retrieves SNMP object nodes in an agent MIB. • Set-The NMS modifies the value of an object node in an agent MIB. • Notifications-Includes traps and informs. SNMP agent sends traps or informs to report events to the NMS. The difference between these two types of notification is that informs require acknowledgement but traps do not. The device supports only traps. SNMP protocol versions HP supports SNMPv1, SNMPv2c, and SNMPv3. An NMS and an SNMP agent must use the same SNMP version to communicate with each other. • SNMPv1-Uses community names for authentication. To access an SNMP agent, an NMS must use the same community name as set on the SNMP agent. If the community name used by the NMS is different from that set on the agent, the NMS cannot establish an SNMP session to access the agent or receive traps from the agent. • SNMPv2c-Uses community names for authentication. SNMPv2c is compatible with SNMPv1, but supports more operation modes, data types, and error codes. • SNMPv3-Uses a user-based security model (USM) to secure SNMP communication. You can configure authentication and privacy mechanisms to authenticate and encrypt SNMP packets for integrity, authenticity, and confidentiality. SNMP configuration task list Task Configuring SNMP basic parameters Switching the NM-specific interface index format Configuring SNMP logging Configuring SNMP traps Remarks Required Optional Optional Optional Configuring SNMP basic parameters SNMPv3 differs from SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c in many ways. Their configuration procedures are described in separate sections. Configuring SNMPv3 basic parameters 53