HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Network Management and Mon - Page 25
Configuration guidelines, Configuration procedure, Disabling an interface from receiving NTP messages
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 25 highlights
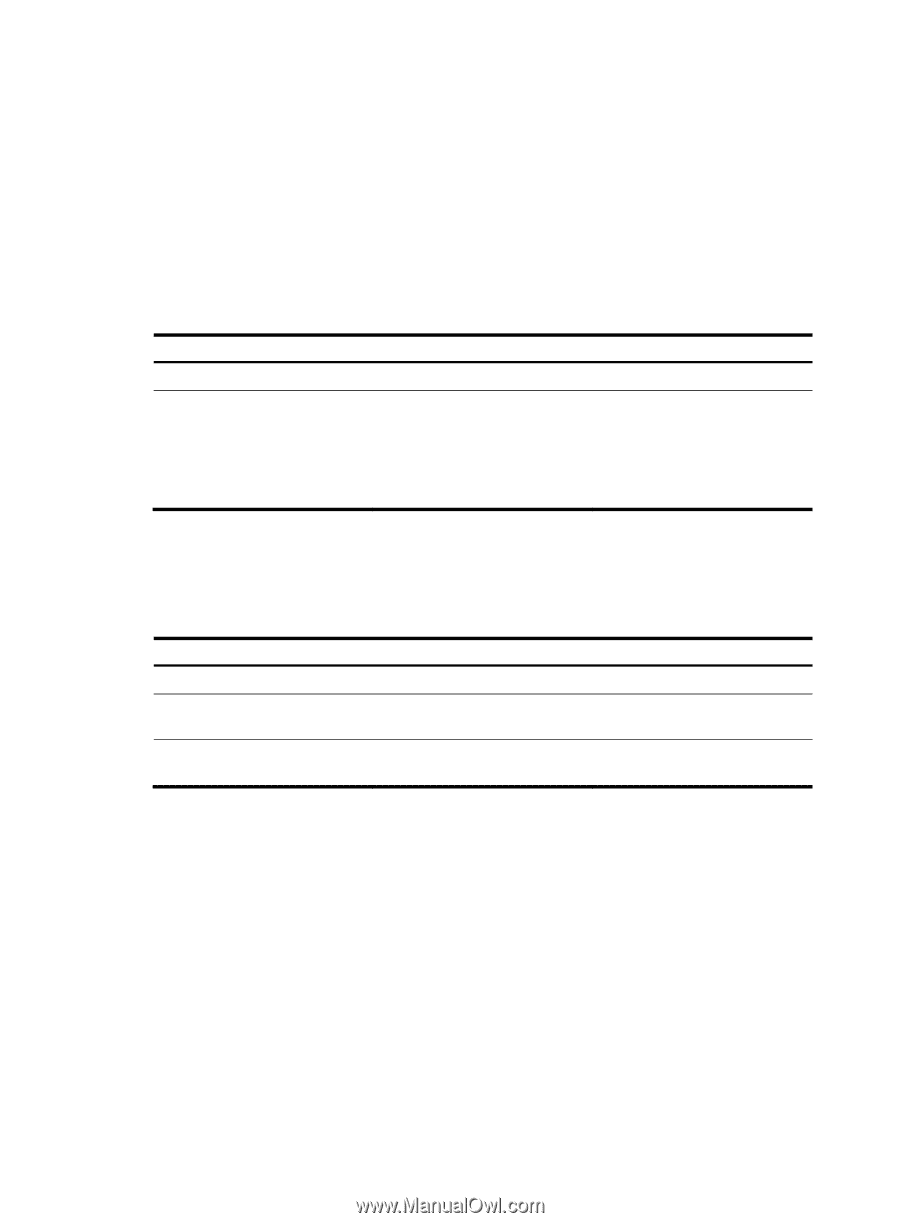
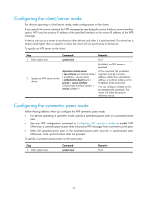
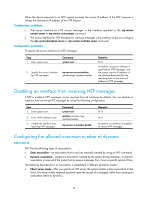
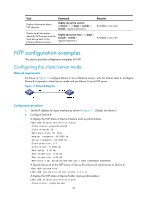
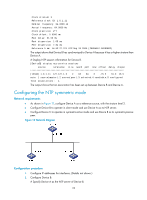
When the device responds to an NTP request received, the source IP address of the NTP response is always the destination IP address of the NTP request. Configuration guidelines • The source interface for NTP unicast messages is the interface specified in the ntp-service unicast-server or ntp-service unicast-peer command. • The source interface for NTP broadcast or multicast messages is the interface where you configure the ntp-service broadcast-server or ntp-service multicast-server command. Configuration procedure To specify the source interface for NTP messages: Step 1. Enter system view. Command system-view 2. Specify the source interface for NTP messages. ntp-service source-interface interface-type interface-number Remarks N/A By default, no source interface is specified for NTP messages, and the system uses the IP address of the interface determined by the matching route as the source IP address of NTP messages. Disabling an interface from receiving NTP messages If NTP is enabled, NTP messages can be received from all interfaces by default. You can disable an interface from receiving NTP messages by using the following configuration. Step 1. Enter system view. 2. Enter VLAN interface view. 3. Disable the interface from receiving NTP messages. Command system-view interface interface-type interface-number ntp-service in-interface disable Remarks N/A N/A By default, an interface is enabled to receive NTP messages. Configuring the allowed maximum number of dynamic sessions NTP has the following types of associations: • Static association-An association that a user has manually created by using an NTP command. • Dynamic association-Temporary association created by the system during operation. A dynamic association is removed if the system fails to receive messages from it over a specific period of time. The following describes how an association is established in different operation modes: • Client/server mode-After you specify an NTP server, the system creates a static association on the client. The server simply responds passively upon the receipt of a message, rather than creating an association (static or dynamic). 18