HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Network Management and Mon - Page 145
Configuring sFlow, sFlow configuration task list
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 145 highlights
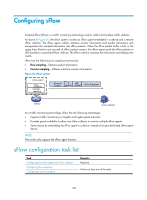
Configuring sFlow Sampled Flow (sFlow) is a traffic monitoring technology used to collect and analyze traffic statistics. As shown in Figure 50, the sFlow system involves an sFlow agent embedded in a device and a remote sFlow collector. The sFlow agent collects interface counter information and packet information and encapsulates the sampled information into sFlow packets. When the sFlow packet buffer is full, or the aging timer (fixed to one second) of sFlow packets expires, the sFlow agent sends the sFlow packets in UDP packets to a specified sFlow collector. The sFlow collector analyzes the information and displays the results. sFlow has the following two sampling mechanisms: • Flow sampling-Obtains packet information. • Counter sampling-Obtains interface counter information. Figure 50 sFlow system sFlow agent Flow sampling Counter sampling Ethernet header IP header UDP header sFlow Datagram Device sFlow collector As a traffic monitoring technology, sFlow has the following advantages: • Supports traffic monitoring on Gigabit and higher-speed networks. • Provides good scalability to allow one sFlow collector to monitor multiple sFlow agents. • Saves money by embedding the sFlow agent in a device, instead of using a dedicated sFlow agent device. NOTE: The switch only supports the sFlow agent function . sFlow configuration task list Task Configuring the sFlow agent and sFlow collector Configuring flow sampling Configuring counter sampling Remarks Required. Perform at least one of the tasks. 138