HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Network Management and Mon - Page 65
Configuring SNMP logging, Enabling SNMP traps
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 65 highlights
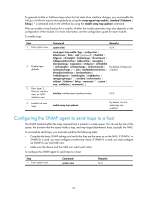
Step 3. Switch the format of an NM-specific ifindex from 32-bit to 16-bit. Command undo snmp-agent ifmib long-ifindex enable Remarks Optional. By default, an NM-specific ifindex is in 16-bit format. Configuring SNMP logging IMPORTANT: Disable SNMP logging in normal cases to prevent a large amount of SNMP logs from decreasing device performance. The SNMP logging function logs Get requests, Set requests, and Set responses, but does not log Get responses. • Get operation-The agent logs the IP address of the NMS, name of the accessed node, and node OID. • Set operation-The agent logs the NMS' IP address, name of accessed node, node OID, variable value, and error code and index for the Set operation. The SNMP module sends these logs to the information center as informational messages. You can configure the information center to output these messages to certain destinations, for example, the console and the log buffer. The total output size for the node field (MIB node name) and the value field (value of the MIB node) in each log entry is 1024 bytes. If this limit is exceeded, the information center truncates the data in the fields. For more information about the information center, see "Configuring the information center." To configure SNMP logging: Step 1. Enter system view. 2. Enable SNMP logging. Command system-view snmp-agent log { all | get-operation | set-operation } Remarks N/A By default, SNMP logging is disabled. Configuring SNMP traps The SNMP agent sends traps to inform the NMS of important events, such as a reboot. Traps fall into generic traps and vendor-specific traps. Generic traps include authentication, coldstart, linkdown, linkup and warmstart. All other traps are vendor-defined. SNMP traps generated by a module are sent to the information center. You can configure the information center to enable or disable outputting the traps from a module by severity and set output destinations. For more information about the information center, see "Configuring information center." Enabling SNMP traps Enable SNMP traps only if necessary. SNMP traps are memory-intensive and may affect device performance. 58