HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Network Management and Mon - Page 69
SNMPv3 configuration example, Network requirements
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 69 highlights
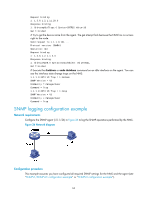
# Enable SNMP traps, set the NMS at 1.1.1.2 as an SNMP trap destination, and use public as the community name. (To make sure the NMS can receive traps, specify the same SNMP version in the snmp-agent target-host command as is configured on the NMS.) [Agent] snmp-agent trap enable [Agent] snmp-agent target-host trap address udp-domain 1.1.1.2 params securityname public v1 [Agent] quit 2. Configure the SNMP NMS: # Configure the SNMP version for the NMS as v1 or v2c, create a read-only community and name it public, and create a read and write community and name it private. For information about configuring the NMS, see the NMS manual. NOTE: The SNMP settings on the agent and the NMS must match. 3. Verify the configuration: # Try to get the count of sent traps from the agent. The attempt succeeds. Send request to 1.1.1.1/161 ... Protocol version: SNMPv1 Operation: Get Request binding: 1: 1.3.6.1.2.1.11.29.0 Response binding: 1: Oid=snmpOutTraps.0 Syntax=CNTR32 Value=18 Get finished # Use a wrong community name to get the value of a MIB node from the agent. You can see an authentication failure trap on the NMS. 1.1.1.1/2934 V1 Trap = authenticationFailure SNMP Version = V1 Community = public Command = Trap Enterprise = 1.3.6.1.4.1.43.1.16.4.3.50 GenericID = 4 SpecificID = 0 Time Stamp = 8:35:25.68 SNMPv3 configuration example Network requirements As shown in Figure 25, the NMS (1.1.1.2/24) uses SNMPv3 to monitor and manage the interface status of the agent (1.1.1.1/24), and the agent automatically sends traps to report events to the NMS. The NMS and the agent perform authentication when they set up an SNMP session. The authentication algorithm is MD5 and the authentication key is authkey. The NMS and the agent also encrypt the SNMP packets between them by using the DES algorithm and the privacy key prikey. 62