HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Network Management and Mon - Page 21
Multicast mode, NTP configuration task list, Configuring NTP operation modes
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 21 highlights
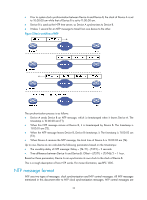
Multicast mode Figure 10 Multicast mode In multicast mode, a server periodically sends clock synchronization messages to the user-configured multicast address, or, if no multicast address is configured, to the default NTP multicast address 224.0.1.1, with the Mode field in the messages set to 5 (multicast mode). Clients listen to the multicast messages from servers. When a client receives the first multicast message, the client and the server start to exchange messages with the Mode field set to 3 (client mode) and 4 (server mode), to calculate the network delay between client and server. Then, the client enters multicast client mode. It continues listening to multicast messages, and synchronizes its local clock based on the received multicast messages. In symmetric peers mode, broadcast mode, and multicast mode, the client (or the symmetric active peer) and the server (the symmetric passive peer) can operate in the specified NTP operation mode only after they exchange NTP messages with the Mode field 3 (client mode) and the Mode field 4 (server mode). During this message exchange process, NTP clock synchronization can be implemented. NTP configuration task list Task Configuring NTP operation modes Configuring optional parameters Configuring access-control rights Configuring NTP authentication Remarks Required Optional Optional Optional Configuring NTP operation modes Devices can implement clock synchronization in one of the following modes: • Client/server mode-Configure only clients. • Symmetric mode-Configure only symmetric-active peers. • Broadcast mode-Configure both clients and servers. • Multicast mode-Configure both clients and servers. 14