HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Network Management and Mon - Page 63
Approach 1 Create an SNMP community, Con the SNMP
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 63 highlights
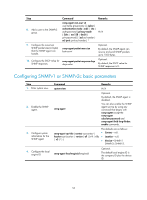
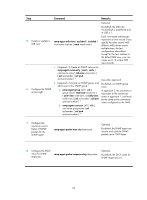
Step Command Remarks Optional. By default, the MIB view ViewDefault is predefined and its OID is 1. 5. Create or update a MIB view. snmp-agent mib-view { excluded | included } view-name oid-tree [ mask mask-value ] Each view-name oid-tree pair represents a view record. If you specify the same record with different MIB subtree masks multiple times, the last configuration takes effect. Except for the four subtrees in the default MIB view, you can create up to 16 unique MIB view records. • (Approach 1) Create an SNMP community: snmp-agent community { read | write } community-name [ mib-view view-name ] [ acl acl-number | acl ipv6 ipv6-acl-number ] * Use either approach. • (Approach 2) Create an SNMP group, and By default, no SNMP group add a user to the SNMP group: exists. 6. Configure the SNMP access right. a. snmp-agent group { v1 | v2c } group-name [ read-view read-view ] In approach 2, the username is equivalent to the community [ write-view write-view ] [ notify-view name in approach 1, and must notify-view ] [ acl acl-number | acl ipv6 be the same as the community ipv6-acl-number ] * name configured on the NMS. b. snmp-agent usm-user { v1 | v2c } user-name group-name [ acl acl-number | acl ipv6 ipv6-acl-number ] * 7. Configure the maximum size (in bytes) of SNMP packets for the SNMP agent. snmp-agent packet max-size byte-count Optional. By default, the SNMP agent can receive and send the SNMP packets up to 1500 bytes. 8. Configure the DSCP value for SNMP responses. snmp-agent packet response dscp dscp-value Optional. By default, the DSCP value for SNMP responses is 0. 56