AMD AMD-K6-2/500AFX Data Sheet - Page 26
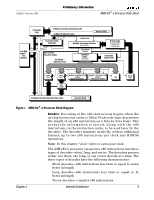
Enhanced RISC86® Microarchitecture, AMD-K6, 2 Processor Block Diagram. - socket 7
 |
View all AMD AMD-K6-2/500AFX manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 26 highlights
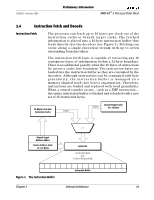
AMD-K6®-2 Processor Data Sheet Preliminary Information 21850J/0-February 2000 Enhanced RISC86® Microarchitecture The Enhanced RISC86 microarchitecture defines the characteristics of the AMD-K6 family. The innovative RISC86 microarchitecture approach implements the x86 instruction set by internally translating x86 instructions into RISC86 operations. These RISC86 operations were specially designed to include direct support for the x86 instruction set while observing the RISC performance principles of fixed length encoding, regularized instruction fields, and a large register set. The Enhanced RISC86 microarchitecture used in the A M D -K 6 -2 p r o c e s s o r e n a b l e s h i g h e r p r o c e s s o r c o re performance and promotes straightforward extensions, such as those added in the current AMD-K6-2 processor and those planned for the future. Instead of directly executing complex x86 instructions, which have lengths of 1 to 15 bytes, the A MD -K 6 -2 proce sso r ex ecute s the si mpl er a nd ea sie r fixed-length RISC86 operations, while maintaining the instruction coding efficiencies found in x86 programs. The AMD-K6-2 processor contains parallel decoders, a centralized RISC86 operation scheduler, and ten execution units that support superscalar operation - multiple decode, execution, and retirement-of x86 instructions. These elements are packed into an aggressive and highly efficient six-stage pipeline. AMD-K6®-2 Processor Block Diagram. As shown in Figure 1 on page 7, the high-performance, out-of-order execution engine of the AMD-K6-2 processor is mated to a split level-one 64-Kbyte writeback cache with 32 Kbytes of instruction cache and 32 Kbytes of data cache. The instruction cache feeds the decoders and, in turn, the decoders feed the scheduler. The ICU issues and retires RISC86 operations contained in the scheduler. The system bus interface is an industry-standard 64-bit Super7 and Socket 7 demultiplexed bus. The AMD-K6-2 processor combines the latest in processor microarchitecture to provide the highest x86 performance for today's personal computers. The AMD-K6-2 processor offers true sixth-generation performance and x86 binary software compatibility. 6 Internal Architecture Chapter 2