Dell PowerEdge 4300 Dell PowerEdge 4300 Systems Installation and Troubleshooti - Page 39
tem board. See Getting
 |
View all Dell PowerEdge 4300 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 39 highlights
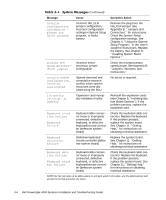
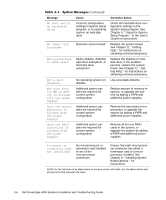
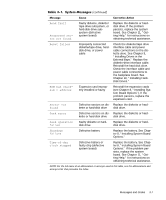
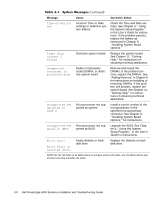
When an error that cannot be reported on the monitor occurs during a boot routine, the computer may emit a series of beeps that identifies the problem. The beep code is a pattern of sounds; for example, one beep followed by a second beep and then a burst of three beeps (code 1-1-3) means that the computer was unable to read the data in nonvolatile random-access memory (NVRAM). This information is valuable to the Dell technical support representative if you need to call for technical assistance. When a beep code is emitted, write it down on a copy of the Diagnostics Checklist found in Chapter 11, "Getting Help," and then look it up in Table 3-2. If you are unable to resolve the problem by looking up the meaning of the beep code, use the Dell Diagnostics to identify a more serious cause (see Chapter 5, "Running the Dell Diagnostics"). If you are still unable to resolve the problem, see Chapter 11, "Getting Help," for instructions on obtaining technical assistance. 1-1-3 1-1-4 1-2-1 1-2-2 NVRAM write/read failure Replace the system board. See Chapter 11, "Getting Help," for instructions on obtaining technical assistance. BIOS checksum failure This fatal error usually requires that you replace the BIOS firmware. See Chapter 11, "Getting Help," for instructions on obtaining technical assistance. Programmable intervaltimer failure DMA initialization failure Replace the system board. See Chapter 11, "Getting Help," for instructions on obtaining technical assistance. 1-2-3 DMA page register write/ read failure 1-3-1 Main-memory refresh verification failure Remove and reseat the DIMMs. If the problem persists, replace the DIMMs. See "Adding Memory" in Chapter 8 for instructions on installing or removing DIMMs. If the problem still persists, replace the system board. See Chapter 11, "Getting Help," for instructions on obtaining technical assistance. NOTE: For the full name of an abbreviation or acronym used in this table, see the abbreviations and acronyms list that precedes the Index. Messages and Codes 3-9