D-Link DGS-3324SR Product Manual - Page 173
RIP Version 1 Message Format, RIP Command Codes, RIP 1 Message, RIP 1 Route Interpretation
 |
UPC - 790069262067
View all D-Link DGS-3324SR manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 173 highlights
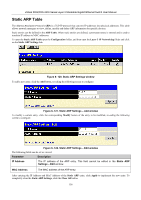
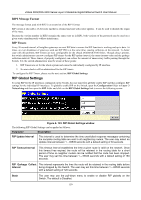
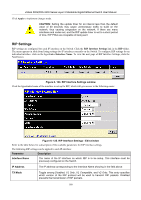
xStack DGS/DXS-3300 Series Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual RIP Version 1 Message Format There are two types of RIP messages: routing information messages and information requests. Both types use the same format. The Command field specifies an operation according the following table: Command Meaning 1 Request for partial or full routing information 2 Response containing network-distance pairs from sender's routing table 3 Turn on trace mode (obsolete) 4 Turn off trace mode (obsolete) 5 Reserved for Sun Microsystem's internal use 9 Update Request 10 Update Response 11 Update Acknowledgement RIP Command Codes The field VERSION contains the protocol version number (1 in this case), and is used by the receiver to verify which version of RIP the packet was sent. RIP 1 Message RIP is not limited to TCP/IP. Its address format can support up to 14 octets (when using IP, the remaining 10 octets must be zeros). Other network protocol suites can be specified in the Family of Source Network field (IP has a value of 2). This will determine how the address field is interpreted. RIP specifies that the IP address, 0.0.0.0, denotes a default route. The distances, measured in router hops are entered in the Distance to Source Network, and Distance to Destination Network fields. RIP 1 Route Interpretation RIP was designed to be used with classed address schemes, and does not include an explicit subnet mask. An extension to version 1 does allow routers to exchange subnetted addresses, but only if the subnet mask used by the network is the same as the subnet mask used by the address. This means the RIP version 1 cannot be used to propagate classless addresses. Routers running RIP version 1 must send different update messages for each IP interface to which it is connected. Interfaces that use the same subnet mask as the router's network can contain subnetted routes, other interfaces cannot. The router will then advertise only a single route to the network. RIP Version 2 Extensions RIP version 2 includes an explicit subnet mask entry, so RIP version 2 can be used to propagate variable length subnet addresses or CIDR classless addresses. RIP version 2 also adds an explicit next hop entry, which speeds convergence and helps prevent the formation of routing loops. 158