D-Link DGS-3324SR Product Manual - Page 92
VLAN and Trunk Groups, Protocol VLANs, Protocol, Type Header in Hexadecimal Form
 |
UPC - 790069262067
View all D-Link DGS-3324SR manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 92 highlights
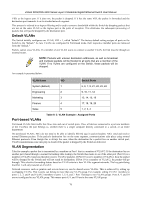
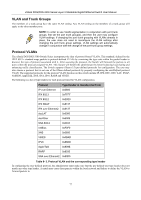
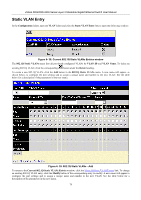
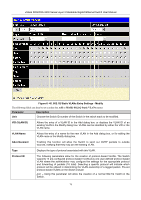
xStack DGS/DXS-3300 Series Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual VLAN and Trunk Groups The members of a trunk group have the same VLAN setting. Any VLAN setting on the members of a trunk group will apply to the other member ports. NOTE: In order to use VLAN segmentation in conjunction with port trunk groups, first set the port trunk group(s), and then the user may configure VLAN settings. If changing the port trunk grouping with VLANs already in place, the user does not need to reconfigure the VLAN settings after changing the port trunk group settings. VLAN settings will automatically change in conjunction with the change of the port trunk group settings. Protocol VLANs The xStack DGS/DXS-3300 Switch Series incorporates the idea of protocol-based VLANs. This standard, defined by the IEEE 802.1v standard maps packets to protocol-defined VLANs by examining the type octet within the packet header to discover the type of protocol associated with it. After assessing the protocol, the Switch will forward the packets to all ports within the protocol-assigned VLAN. This feature will benefit the administrator by better balancing load sharing and enhancing traffic classification. The Switch supports fifteen (15) pre-defined protocols for configuration. The user may also choose a protocol that is not one of the fifteen defined protocols by properly configuring the userDefined protocol VLAN. The supported protocols for the protocol VLAN function on this switch include IP, IPX, DEC, DEC LAT, SNAP, NetBIOS, AppleTalk, XNS, SNA, IPv6, RARP and VINES. The following is a list of type headers for each protocol listed for VLAN configuration. Protocol IP over Ethernet Type Header in Hexadecimal Form 0x0800 IPX 802.3 0xFFFF IPX 802.2 0xE0E0 IPX SNAP 0x8137 IPX over Ethernet2 0x8137 decLAT 0x6000 decOther 0x6009 SNA 802.2 0x0404 netBios 0xF0F0 XNS VINES IPV6 0x0600 0x0BAD 0x86DD AppleTalk 0x809B RARP 0x8035 SNA over Ethernet2 0x80D5 Table 6- 3. Protocol VLAN and the corresponding type header In configuring the user-defined protocol, the administrator must make sure that the pre-defined user type header does not match any other type header. A match may cause discrepancies within the local network and failure to define the VLAN to forward packets to. 77