D-Link DGS-3324SR Product Manual - Page 184
Hello Packet, This router's Router Priority. The Router Priority is used in
 |
UPC - 790069262067
View all D-Link DGS-3324SR manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 184 highlights
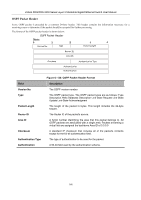
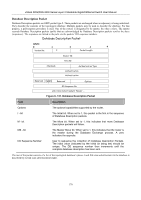
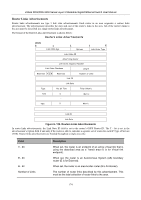
xStack DGS/DXS-3300 Series Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual Hello Packet Hello packets are OSPF packet type 1. They are sent periodically on all interfaces, including virtual links, in order to establish and maintain neighbor relationships. In addition, Hello Packets are multicast on those physical networks having a multicast or broadcast capability, enabling dynamic discovery of neighboring routers. All routers connected to a common network must agree on certain parameters such as the Network Mask, the Hello Interval, and the Router Dead Interval. These parameters are included in the hello packets, so that differences can inhibit the forming of neighbor relationships. A detailed explanation of the receive process for Hello packets is necessary so that differences can inhibit the forming of neighbor relationships. The format of the Hello packet is shown below: Hello Packet Version No. 1 Packet Length Router ID Area ID Checksum Authentication Type Authentication Authentication Network Mask Hello Interval Options Router Dead Interval Router Priority Designated Router Backup Designated Router Neighbor Figure 6- 130. Hello Packet Field Network Mask Options Hello Interval Router Priority Router Dead Interval Designated Router Backup Designated Router Field Neighbor Description The network mask associated with this interface. The optional capabilities supported by the router. The number of seconds between this router's Hello packets. This router's Router Priority. The Router Priority is used in the election of the DR and BDR. If this field is set to 0, the router is ineligible become the DR or the BDR. The number of seconds that must pass before declaring a silent router as down. The identity of the DR for this network, in the view of the advertising router. The DR is identified here by its IP interface address on the network. The identity of the Backup Designated Router (BDR) for this network. The BDR is identified here by its IP interface address on the network. This field is set to 0.0.0.0 if there is no BDR. Description The Router IDs of each router from whom valid Hello packets have been seen within the Router Dead Interval on the network. 169