D-Link DGS-3324SR Product Manual - Page 186
Link-State Request Packet, Link-State Request Packet
 |
UPC - 790069262067
View all D-Link DGS-3324SR manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 186 highlights
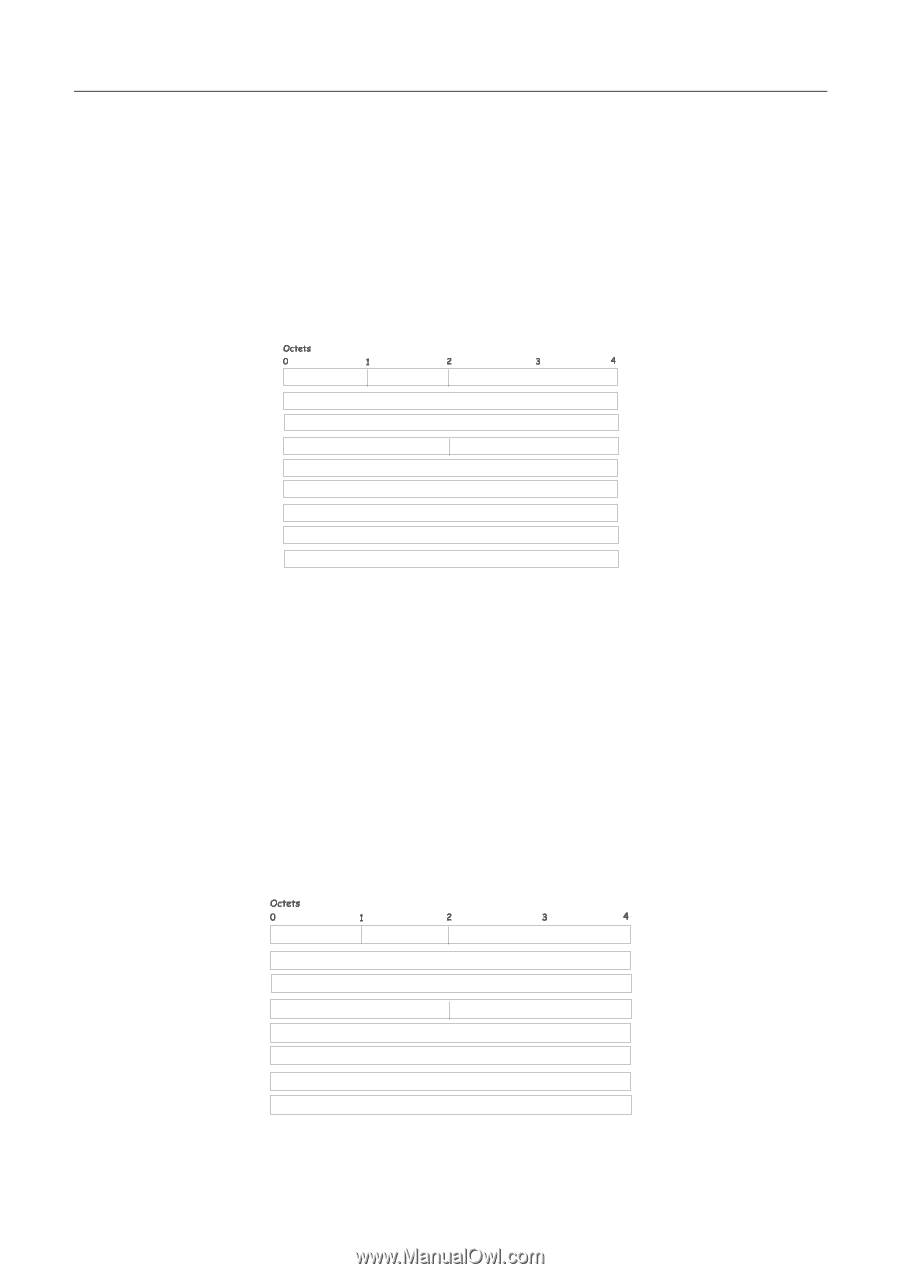
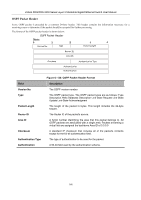
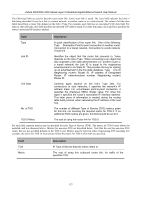
xStack DGS/DXS-3300 Series Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual Link-State Request Packet Link-State Request packets are OSPF packet type 3. After exchanging Database Description packets with a neighboring router, a router may find that parts of its topological database are out of date. The Link-State Request packet is used to request the pieces of the neighbor's database that are more up to date. Multiple Link-State Request packets may need to be used. The sending of Link-State Request packets is the last step in bringing up an adjacency. A router that sends a Link-State Request packet has in mind the precise instance of the database pieces it is requesting, defined by LS sequence number, LS checksum, and LS age, although these fields are not specified in the Link-State Request packet itself. The router may receive even more recent instances in response. The format of the Link-State Request packet is shown below: Link-State Request Packet Version No. 3 Packet Length Router ID Area ID Checksum Authentication Type Authentication Authentication Link-State Type Link-State ID Advertising Router Figure 6- 132. Link-State Request Packet Each advertisement requested is specified by its Link-State Type, Link-State ID, and Advertising Router. This uniquely identifies the advertisement, but not its instance. Link-State Request packets are understood to be requests for the most recent instance. Link-State Update Packet Link-State Update packets are OSPF packet type 4. These packets implement the flooding of link-state advertisements. Each Link-State Update packet carries a collection of link-state advertisements one hop further from its origin. Several link-state advertisements may be included in a single packet. Link-State Update packets are multicast on those physical networks that support multicast/broadcast. In order to make the flooding procedure reliable, flooded advertisements are acknowledged in Link-State Acknowledgment packets. If retransmission of certain advertisements is necessary, the retransmitted advertisements are always carried by unicast LinkState Update packets. The format of the Link-State Update packet is shown below: Link-State Update Packet Version No. 4 Packet Length Router ID Area ID Checksum Authentication Type Authentication Authentication Number of Advertisements Link-State Advertisements ... Figure 6- 133. Link-State Update Packet 171