Dell PowerConnect Brocade M6505 Brocade 7.1.0 Web Tools Administrator's Guide - Page 217
Transport mode and tunnel mode, Table 17,
 |
View all Dell PowerConnect Brocade M6505 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 217 highlights
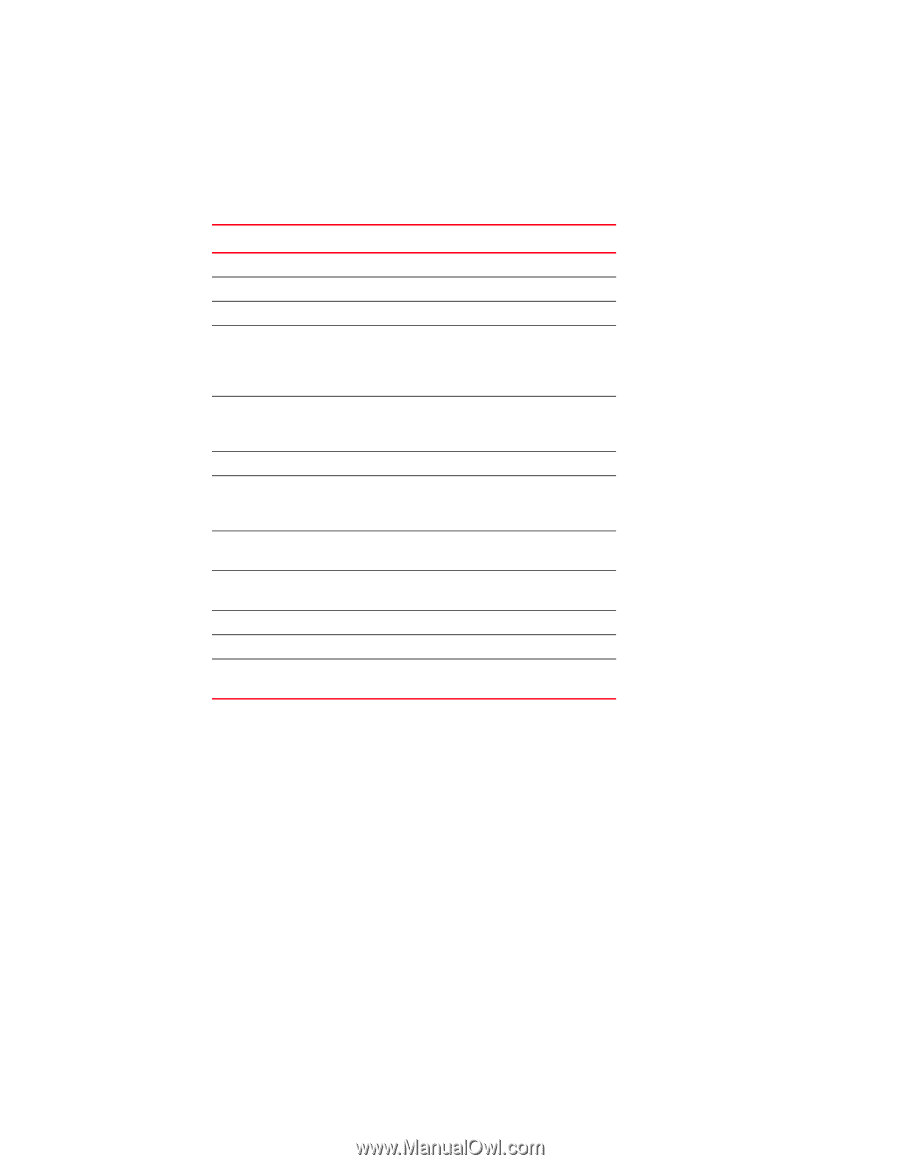
IPsec concepts 15 There are several protocols and algorithms that can be applied. Choosing the protocols and algorithms you want to use may be a matter of adapting to an implementation that is already in place in your LAN, or you may need to do a significant amount of research and planning. The supported protocols and algorithms are defined and described in the RFCs listed in Table 17. TABLE 17 Relevant RFCs RFC number Title RFC 4301 RFC 4302 RFC 4303 RFC 4304 RFC 4305 RFC 4869 RFC 4309 RFC 4306 RF C4307 RFC 3971 RFC 3972 RFC 3041 Security Architecture for the Internet Protocol IP Authentication Header IP Encapsulating Security Payload Extended Sequence Number (ESN) Addendum to IPsec Domain of Interpretation (DOI) for Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol (ISAKMP) Cryptographic Algorithm Implementation Requirements for Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) and Authentication Header Suite B Cryptographic Suites for IPsec Using Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) CCM Mode with IPsec Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) Internet Key Exchange Version 2 (IKEv2) Protocol Cryptographic Algorithms for Internet Key Exchange Version 2 (IKEv2) Secure Neighbor Discovery Cryptographically Generated Addresses Privacy Extensions for Stateless Address Auto configuration in IPv6 Transport mode and tunnel mode Transport mode adds an authentication header (AH) before the IP header. Only a single pair of addresses is used (those in the IP header). When transport mode is used, both endpoints implement IPsec. Tunnel mode encapsulates an IP datagram in a new datagram, with a new IP header specifying the addresses of the tunnel end points. IPsec is implemented between tunnel endpoints. IPsec is transparent to the actual endpoints within the IP header in the original packet. Figure 41 provides a basic visual comparison of how transport mode and tunnel mode modify an IP datagram. Web Tools Administrator's Guide 189 53-1002756-01