HP BladeSystem bc2800 Embedded Web System User Guide for the HP BladeSystem PC - Page 111
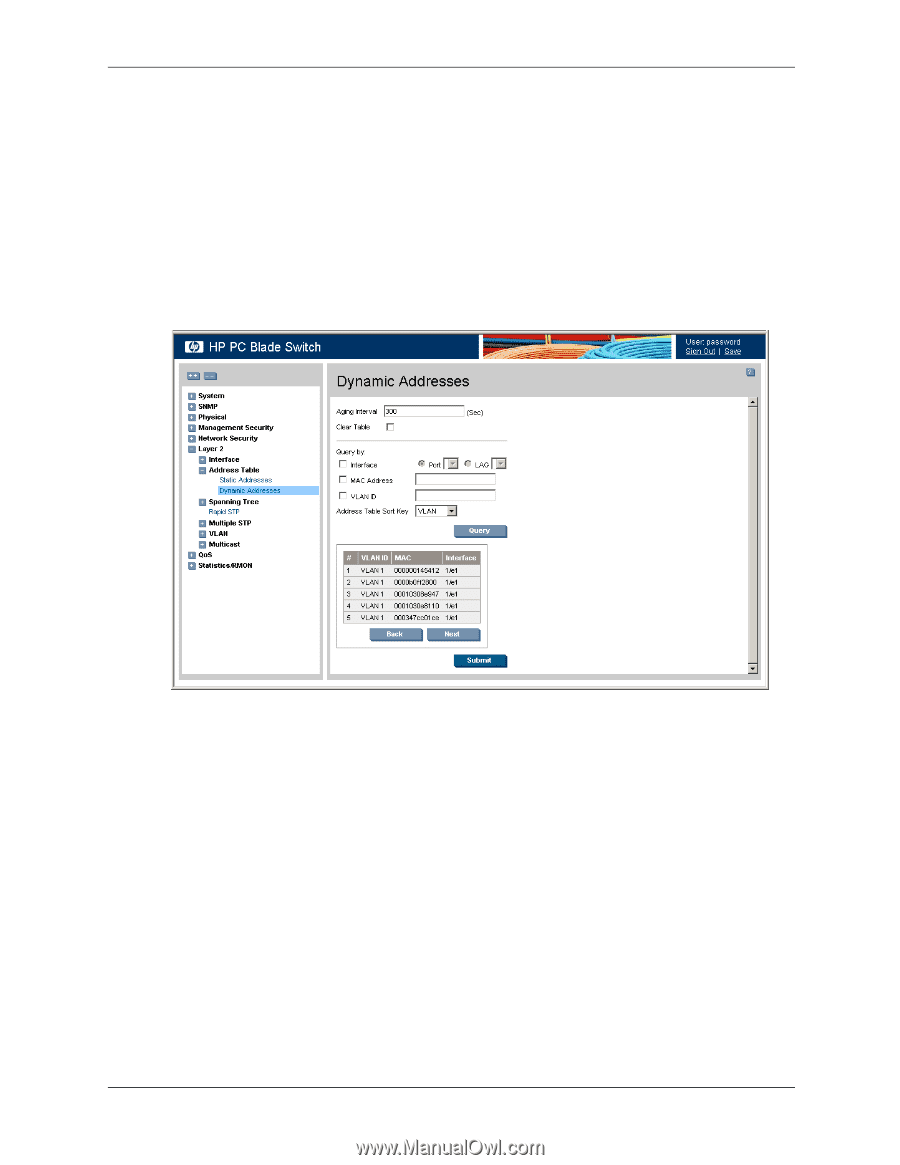
Defining Dynamic Forwarding Database Entries
 |
View all HP BladeSystem bc2800 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 111 highlights
Defining the Forwarding Database Defining Dynamic Forwarding Database Entries The Dynamic Addresses page contains parameters for querying information in the Dynamic MAC Address Table, including the interface type, MAC addresses, VLAN, and table storing. The Dynamic MAC Address table contains information about the aging time before a dynamic MAC address is erased, and includes parameters for querying and viewing the Dynamic MAC Address table. The Dynamic MAC Address table contains address parameters by which packets are directly forwarded to the ports. The Dynamic Address Table can be sorted by interface, VLAN, and MAC Address. To configure the Dynamic MAC Address table: 1. Click Layer 2 > Address Table > Dynamic Addresses. Dynamic Addresses The Dynamic Addresses page contains the following fields: ❏ Aging Interval (secs) - Specifies the amount of time in seconds the MAC address remains in the Dynamic MAC Address table before it is timed out, if no traffic from the source is detected. The default value is 300 seconds. ❏ Clear Table - Clears the Dynamic Addresses Table. The possible field values are: ◆ Checked - Clears the Dynamic Address Table. ◆ Unchecked - Maintains the Dynamic Address Table entries. This is the default value. ❏ Interface - Defines the interface type by which the dynamic addresses are sorted. There are two interface types from which to select: ◆ Port - Specifies the port number for which the forwarding database parameters refer. ◆ LAG - The specific LAG number to which the forwarding database parameters refer. Embedded Web System User Guide www.hp.com 8-3