HP BladeSystem bc2800 Embedded Web System User Guide for the HP BladeSystem PC - Page 135
Configuring SNMP
 |
View all HP BladeSystem bc2800 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 135 highlights
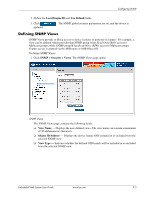
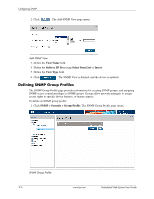
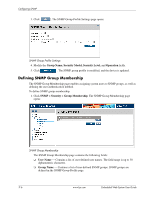
11 Configuring SNMP Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) provides a method for managing network devices. The device supports the following SNMP versions: ■ SNMP version 1 ■ SNMP version 2c ■ SNMP version 3 SNMP v1 and v2c The SNMP agents maintain a list of variables, which are used to manage the device. The variables are defined in the Management Information Base (MIB). The SNMP agent defines the MIB specification format, as well as the format used to access the information over the network. Access rights to the SNMP agents are controlled by access strings. SNMP v3 SNMP v3 applies access control and a new traps mechanism. In addition, User Security Model (USM) parameters are defined for SNMPv3, including: ■ Authentication - Provides data integrity and data origin authentication. ■ Privacy - Protects against the disclosure of message content. Cipher Block-Chaining (CBC) is used for encryption. Either authentication is enabled on an SNMP message, or both authentication and privacy are enabled on an SNMP message. However, privacy cannot be enabled without authentication. ■ Timeliness - Protects against message delay or message redundancy. The SNMP agent compares incoming messages to the message time information. ■ Key Management - Defines key generation, key updates, and key use. The device supports SNMP notification filters based on Object IDs (OIDs). OIDs are used by the system to manage device features. SNMP v3 supports the following features: Security, Feature Access Control, and Traps. The device generates copy traps. This section contains the following topics: ■ Configuring SNMP Security ■ Configuring SNMP Notifications Embedded Web System User Guide www.hp.com 11-1