HP BladeSystem bc2800 Embedded Web System User Guide for the HP BladeSystem PC - Page 48
Configuring Network Security
 |
View all HP BladeSystem bc2800 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 48 highlights
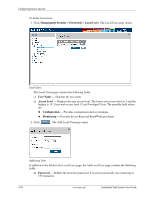
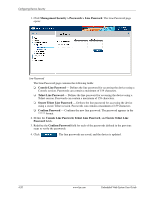
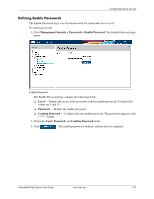
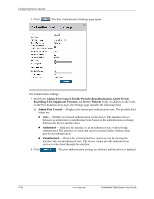
Configuring Device Security Configuring Network Security Network security manages both access control lists and locked ports. This section contains the following topics: ■ Network Security Overview ■ Defining Port Authentication Properties ■ Defining Port Authentication ■ Configuring Traffic Control Network Security Overview This section provides an overview of network security and contains the following topics: ■ Port-Based Authentication ■ Advanced Port-Based Authentication Port-Based Authentication Port-based authentication authenticates users on a per-port basis using an external server. Only authenticated and approved system users can transmit and receive data. Ports are authenticated via the RADIUS server using the Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP). Port-based authentication includes: ■ Authenticators - Specifies the device port which is authenticated before permitting system access. ■ Supplicants - Specifies the host connected to the authenticated port requesting to access the system services. ■ Authentication Server - Specifies the server that performs the authentication on behalf of the authenticator, and indicates whether the supplicant is authorized to access system services. Port-based authentication creates two access states: ■ Controlled Access - Permits communication between the supplicant and the system, if the supplicant is authorized. ■ Uncontrolled Access - Permits uncontrolled communication regardless of the port state. The device currently supports port-based authentication using RADIUS servers. Advanced Port-Based Authentication Advanced port-based authentication enables multiple hosts to be attached to a single port. Advanced port-based authentication requires only one host to be authorized for all hosts to have system access. If the port is unauthorized, all attached hosts are denied access to the network. Advanced port-based authentication also enables user-based authentication. Specific VLANs in the device are always available, even if specific ports attached to the VLAN are unauthorized. For example, Voice over IP does not require authentication, while data traffic requires authentication. VLANs for which authorization is not required can be defined. Unauthenticated VLANs are available to users, even if the ports attached to the VLAN are defined as authorized. 4-22 www.hp.com Embedded Web System User Guide