HP LaserJet MFP M72625-M72630 User Guide - Page 172
The Transmission Control Protocol TCP and the Internet Protocol IP are the set of communications
 |
View all HP LaserJet MFP M72625-M72630 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 172 highlights
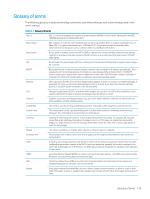
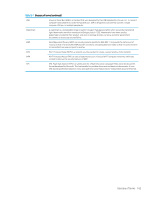
Table B-1 Glossary of terms (continued) Printer Driver A program used to send commands and transfer data from the computer to the printer. Print Media Media like paper, envelopes, labels, and transparencies which can be used in a printer, scanner, fax, or copier. PPM Pages Per Minute (PPM) is a method of measurement for determining how fast a device works, meaning the number of pages a device can produce in one minute. PRN file An interface for a device driver, this allows software to interact with the device driver using standard input / output system calls, which simplifies many tasks. Protocol A convention or standard that controls or enables the connection, communication, and data transfer between two computing endpoints. PSTN The Public-Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) is the network of the world's public circuit-switched telephone networks which, on industrial premises, is usually routed through the switchboard. Quick copy Quick copy menu allows you to quickly set copy options without having to move to a lower level menu or another tab. This option does not provide all copy options. Resolution The sharpness of an image, measured in Dots Per Inch (DPI). The higher the DPI, the greater the resolution. SEF Short Edge Feed, the media is loaded into the cassette tray where the short side of the paper is fed into the device first. SMB Server Message Block (SMB) is a network protocol mainly applied to share files, printers, serial ports, and miscellaneous communications between nodes on a network. SMB also provides an authenticated Inter- process communication mechanism. SMTP Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) is the standard for email transmissions across the internet. SMTP is a relatively simple, text-based protocol, where one or more recipients of a message are specified and the message text is transferred. It is a client server protocol where the client transmits an email message to the server. SSID Service Set Identifier (SSID) is a name of a wireless local area network (WLAN). All wireless devices in the WLAN use the same SSID in order to communicate with each other. The SSIDs are case-sensitive and have a maximum length of 32 characters. Stamp Allows the printing of some information such as date and time, page number, ID, IP address, and comments. Subnet Mask The subnet mask is used in conjunction with the network address to determine which part of the address is the network address and which part is the host address. TCP / IP The Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and the Internet Protocol (IP) are the set of communications protocols that implement the protocol stack on which the internet and most commercial networks run. TIFF Tagged Image File Format (TIFF) is a variable-resolution bitmapped image format. TIFF describes image data that typically come from scanners. TIFF images use tags, keywords defining the characteristics of the image that is included in the file. This flexible and platform-independent format can be used for pictures that have been made by various image processing applications. Toner Cartridge A bottle or container that holds toner, which is used in a device like a printer. Toner is a powder used in laser printers and photocopiers. The toner forms the text and images on printed paper. Toner can be fused by a combination of heat/pressure from the fuser, causing it to bind the fibers in the paper. Toner collection unit A container that holds contaminated toner. Tray 1 (MP) The Tray 1 multi-purpose (MP) tray can hold special sizes and types of print material, such as postcards note cards and envelopes. It is useful for single page printing on colored paper. TWAIN An industry standard for scanners and software. By using a TWAIN compliant scanner with TWAIN-compliant software, a scan can be initiated from the program. TWAIN is an image capture API for Microsoft Windows and Apple Macintosh operating systems. URL Uniform Resource Locator (URL) is the global address of documents and resources on the internet. The first part of the address indicates what protocol to use. The second part specifies the IP address or the domain name where the resource is located. 162 Appendix B Glossary