Netgear GS516TP Software Administration Manual - Page 138
MAC ACL, MAC Rules, Security > ACL > Basic > MAC Rules
 |
View all Netgear GS516TP manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 138 highlights
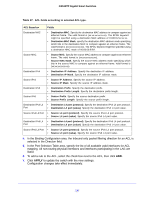
GS516TP Gigabit Smart Switches MAC ACL A MAC ACL consists of a set of rules that are matched sequentially against a packet. When a packet meets the match criteria of a rule, the specified rule action (permit or deny) is taken and the additional rules are not checked for a match. The steps for defining a MAC ACL and applying it to the switch are described in the following sections: 1. Use the MAC ACL screen to create the ACL ID. 2. Use the MAC Rules screen to create rules for the ACL. 3. Use the MAC Binding Configuration screen to assign the ACL by its ID number to a port. 4. Optionally, use the MAC Binding Table screen to view the configurations. To configure a MAC ACL: 1. Select Security > ACL > Basic > MAC ACL. 2. Specify a name for the MAC ACL in the Name field. The name string can include alphabetic, numeric, hyphen, underscore, or space characters only. The name must start with an alphabetic character. 3. Click ADD. Each configured ACL displays the following information: • Rules. Displays the number of rules currently configured for the MAC ACL. • Direction. Displays the direction of packet traffic affected by the MAC ACL, which can be Inbound or blank. To change the name of a MAC ACL, select the check box next to the Name field, update the name, then click APPLY. MAC Rules Use the MAC Rules screen to define rules for MAC-based ACLs. The access list definition includes rules that specify whether traffic matching the criteria is forwarded normally or discarded. A default 'deny all' rule is the last rule of every list. To configure MAC ACL rules: 1. Select Security > ACL > Basic > MAC Rules. 2. From the ACL Name field, specify the existing MAC ACL to which the rule applies. For information about how to set up a new MAC ACL, use the MAC ACL screen. 3. In the ID field, enter an ID for the rule. The valid range is 1-10. 4. Configure the following settings: • Action. Specify what action must be taken if a packet matches the rule's criteria. • Permit. Forwards packets that meet the ACL criteria. • Deny. Drops packets that meet the ACL criteria. 138