HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch Fundamentals Configuration Guide - Page 130
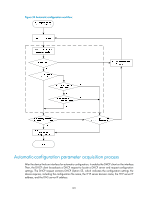
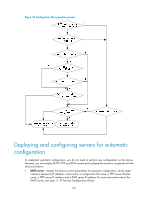
Configuration file acquisition process, Option 67, network.cfg
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 130 highlights
After the device obtains an IP address, it resolves the received DHCP reply to examine the following fields: • Option 67 or the file field-Carries the configuration file name. The device resolves Option 67 first. If Option 67 does not contain the configuration file name, the device resolves the file field. • Option 12-Carries the host name. This host name might be used to determine the configuration file name, which is in the format host name.cfg. • Option 150-Carries the TFTP server IP address. If this option contains a valid TFTP server IP address, the device starts the configuration file acquisition process. Otherwise, the device resolves Option 66. • Option 66-Carries the TFTP server domain name. If Option 150 does not contain a TFTP server IP address, the device resolves this option for a TFTP server domain name and tries to communicate with the DNS server indicated by Option 6 to get the TFTP server IP address. • Option 6-Carries the DNS server IP address. For more information about DHCP, see Layer 3-IP Services Configuration Guide. Configuration file acquisition process During the automatic-configuration parameter acquisition process, the device might or might not get a TFTP server IP address: • If the device gets a TFTP server IP address, it starts the configuration file acquisition process by unicasting a request to the TFTP server. • If not, the device starts the configuration file acquisition process by broadcasting a request. In this case, the device resolves only the first reply. As shown in Figure 33, the device determines what to request from the TFTP server based on whether or not it got a configuration file name during the automatic-configuration parameter acquisition process: • If the device got a configuration file name, it requests the specified configuration file. • If not, it requests a configuration file named in the format host name.cfg from the TFTP server, where host name represents the host name of the device. If the device got no host name during the automatic-configuration parameter acquisition process, it first requests the host name file network.cfg, which contains mappings between IP addresses and host names. If the device fails to get the host name file or the file contains no entry for the device's temporary IP address, it tries to communicate with a DNS server to resolve the temporary IP address to a host name. After the device gets the host name, it tries to obtain the configuration file for the host name. If the device fails to get a configuration file specific for itself, it requests the default configuration file device.cfg from the TFTP server. 123