HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch Fundamentals Configuration Guide - Page 80
Configuring TFTP, FIPS compliance, Configuring the device as an IPv4 TFTP client
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 80 highlights
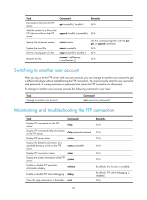
Configuring TFTP Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) is a simplified version of FTP for file transfer over secure reliable networks. TFTP uses UDP port 69 for data transmission. In contrast to TCP-based FTP, TFTP does not require authentication or complex message exchanges, and is easier to deploy. TFTP is suited for reliable network environments. The device can only operate as a TFTP client. You can upload a file from the device to the TFTP server or download a file from the TFTP server to the device. If you download a file with a file name that exists in the target directory, the device deletes the existing file and saves the new one. If file download fails due to network disconnection or other reasons, the original file cannot be restored. Therefore, use a nonexistent file name instead. Figure 23 TFTP application scenario FIPS compliance The device supports the FIPS mode that complies with NIST FIPS 140-2 requirements. Support for features, commands, and parameters might differ in FIPS mode and non-FIPS mode. For more information about FIPS mode, see Security Configuration Guide. TFTP is not supported in FIPS mode. Configuring the device as an IPv4 TFTP client Step 1. Enter system view. 2. (Optional.) Use an ACL to control the client's access to TFTP servers. Command system-view tftp-server acl acl-number 3. Specify the source IP address for TFTP packets sent by the TFTP client. tftp client source { interface interface-type interface-number | ip source-ip-address } 4. Return to user view. quit Remarks N/A By default, no ACL is used for access control. By default, no source IP address is specified, and the primary IP address of the output interface is used as the source IP address. N/A 73