HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch Fundamentals Configuration Guide - Page 43
Controlling user access, FIPS compliance, Controlling Telnet/SSH logins
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 43 highlights
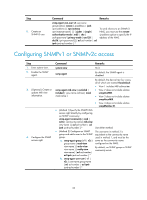
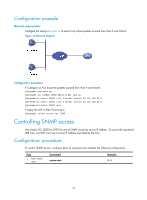
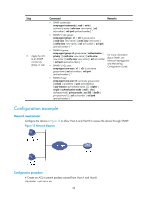
Controlling user access Use ACLs to prevent unauthorized access and configure command authorization and accounting to monitor and control user behaviors. For more information about ACLs, see ACL and QoS Configuration Guide. FIPS compliance The device supports the FIPS mode that complies with NIST FIPS 140-2 requirements. Support for features, commands, and parameters might differ in FIPS mode and non-FIPS mode. For more information about FIPS mode, see Security Configuration Guide. Unless otherwise noted, devices in the configuration examples are operating in non-FIPS mode. Controlling Telnet/SSH logins Use basic ACLs (2000 to 2999) to filter Telnet and SSH logins by source IP address. Use advanced ACLs (3000 to 3999) to filter Telnet and SSH logins by source and/or destination IP address. Use Ethernet frame header ACLs (4000 to 4999) to filter Telnet and SSH logins by source MAC address. If an applied ACL does not exist or has no rules, no user login restriction is applied. If the ACL exists and has rules, only users permitted by the ACL can access the device through Telnet or SSH. Controlling Telnet logins (not supported in FIPS mode) To control Telnet logins: Step 1. Enter system view. 2. Apply an ACL to filter Telnet logins. Command system-view • telnet server acl acl-number • telnet server ipv6 acl { layer2-acl-number | ipv6 ipv6-acl-number } Remarks N/A By default, no ACL is used to filter Telnet logins. Controlling SSH logins Step 1. Enter system view. Command system-view 2. Apply an ACL to filter • ssh server acl acl-number SSH logins. • ssh server ipv6 acl [ ipv6 ] acl-number 36 Remarks N/A By default, no ACL is used to filter SSH logins. For more information about these two commands, see Security Command Reference.