HP t310 PCoIP Administrator's Guide - Page 109
Using the Diagnostic Tools, 6.1 Viewing and Clearing Event Log Messages, 6.1.1 Syslog Features
 |
View all HP t310 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 109 highlights
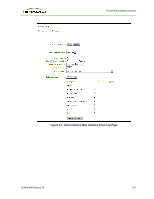
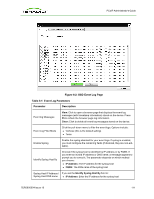
PCoIP Administrator's Guide 6 Using the Diagnostic Tools The Diagnostic menu contains links to pages with run-time information and functions that may be useful for troubleshooting. Note: The Diagnostic options in the OSD are a subset of those available through the Administrative Web Interface. 6.1 Viewing and Clearing Event Log Messages The Event Log page lets you view and clear event log messages from the host or client. The web interface lets you change the log filter setting on the device, which controls which messages are put in the log. When you set the filter to "terse", the device logs terse messages. The Event Log page also lets you enable and define syslog as a way of collecting and reporting your events that meets the IETF standard for logging program messages. 6.1.1 Syslog Features l Allows separation of the software that generates messages from the system that stores them and the software that reports and analyzes them. l Provides devices that would otherwise be unable to communicate a way to notify administrators of problems or performance. l Can be used for computer system management and security auditing as well as generalized informational, analysis, and debugging messages. l Is supported by a wide variety of devices and receivers across multiple platforms. l Can be used to integrate log data from many different types of systems into a central repository. l Has messages that: o refer to a facility (auth, authpriv, daemon, cron, ftp, lpr, kern, mail, news, syslog, user, uucp, local0, ... , local7 ) . o are assigned a priority/level (Emergency, Alert, Critical, Error, Warning, Notice, Info or Debug) by the sender of the message. l Lets you direct messages to various local devices (console), files (/var/log/) or remote syslog daemons. Note: Take care when you update the configuration as omitting or misdirecting message facilities or levels can cause important messages to be ignored by syslog or overlooked by the administrator. TER0606004 Issue 16 109