D-Link DNS-1250-04 Acronis Backup Software User Manual for DNS-1250-04 - Page 20
Full backups
 |
View all D-Link DNS-1250-04 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 20 highlights
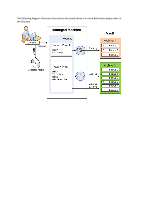
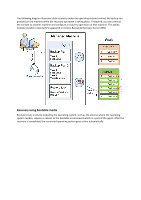
If the machine fails to boot or you need to recover data to bare metal, you boot the machine using the bootable media and configure the recovery operation in the same way as the recovery task. The following diagram illustrates the recovery using the bootable media. 2.2 Full backups Acronis Backup & Recovery Server OEM provides the capability to create custom backup schemes. All backup schemes are based on full backup method. The term "scheme" in fact denotes the algorithm of applying these methods plus the algorithm of the archive cleanup. Comparing backup methods with each other does not make much sense because the methods work as a team in a backup scheme. Each method should play its specific role according to its advantages. A competent backup scheme will benefit from the advantages of all backup methods and lessen the influence of all the methods' shortcomings. Full backup A full backup stores all data selected for backup. An archive can contain multiple full backups or consist of only full backups. A full backup is self-sufficient - you do not need access to any other backup to recover data from a full backup. It is widely accepted that a full backup is the slowest to do but the fastest to restore. A full backup is most useful when: you need to roll back the system to its initial state this initial state does not change often, so there is no need for regular backup. Example: An Internet cafe, school or university lab where the administrator often undoes changes made by the students or guests but rarely updates the reference backup (in fact, after installing