Dell PowerConnect W-IAP92 Dell Instant 6.1.3.4-3.1.0.0 User Guide - Page 229
DHCP Server Configuration, NAT DHCP Configuration,
 |
View all Dell PowerConnect W-IAP92 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 229 highlights
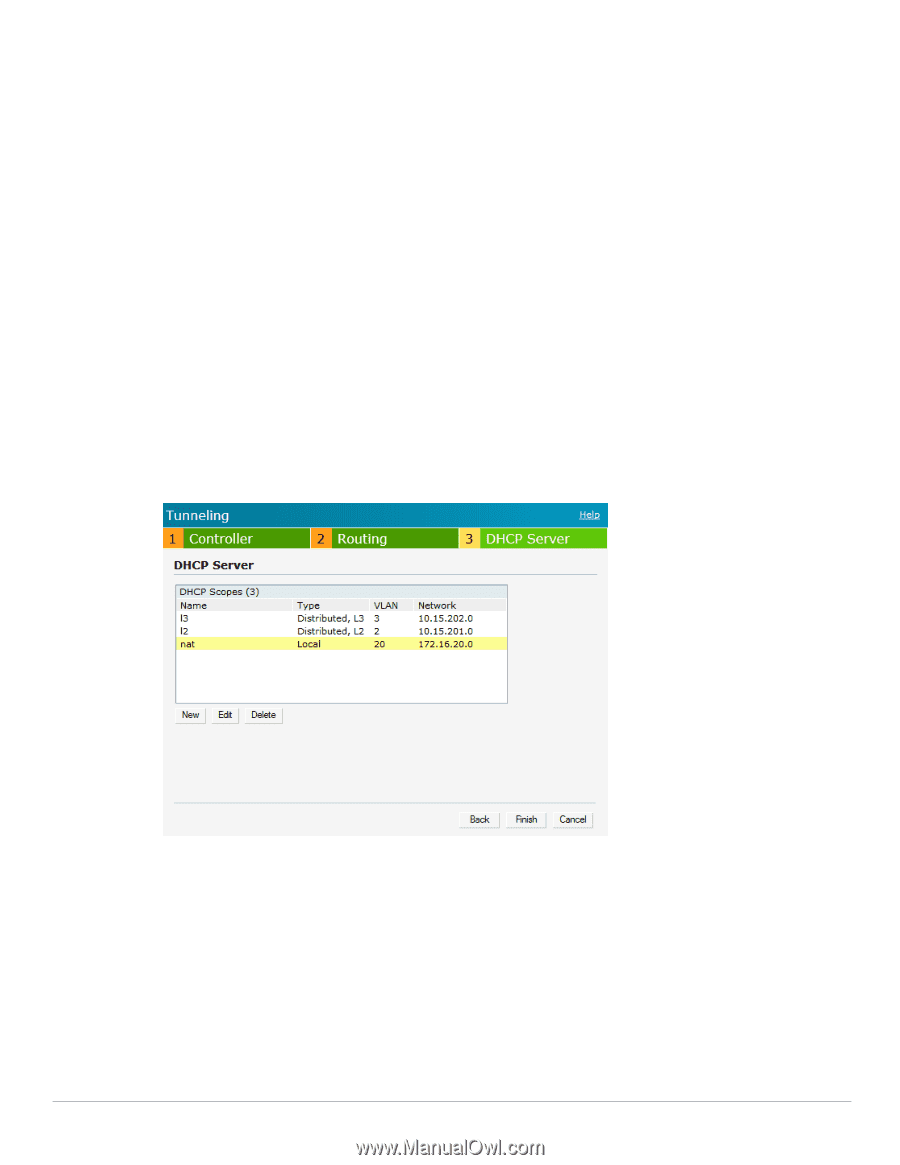
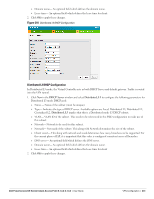
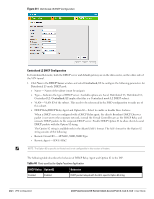
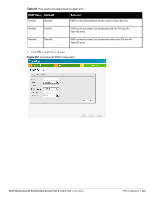
DHCP Server Configuration The Virtual Controller (VC) on an Instant AP enables different DHCP pools (various deployment models) in addition to allocating IP subnets to each branch. The following modes of DHCP server are supported: Local Subnet- In this mode, the VC assigns an IP address from a configured subnet and forwards traffic to both corporate and non-corporate destinations. This is achieved by appropriately translating the network address (NAT) and forwarding the packet through the IPSec tunnel or through the uplink. L2 Switching Mode- In this mode, Instant supports the following two types to support L2 switching mode of connection to corporate: Distributed L2- In this mode, the VC assigns an IP address from a configured subnet and forwards traffic to both corporate and non-corporate destinations. The VC adds the VLAN configured in this subnet to the controller VLAN multicast table enabling the L2 subnet to act as an extension of the VLAN on the controller. Corporate traffic is sent on the IPSec tunnel and non-corporate traffic is sent on the uplink. Centralized L2- In this mode, the VC does not assign an IP address to the client, but the DHCP traffic is directly forwarded to the controller over the IPSec tunnel and gets an IP address from either the controller or a DHCP server behind the controller serving the VLAN of the client. However, Instant AP does forward client traffic in the same way as the Distributed L2 mode. L3 Routing Mode- In this mode, Instant supports L3 routing mode of connection to corporate. VC assigns an IP addresses from the configured subnet and forwards traffic to both corporate and non-corporate destinations. Instant AP takes care of routing on the subnet and also adds a route on the controller after the VPN tunnel is set up during the registration of the subnet. Figure 208 Tunneling- DHCP Server NAT DHCP Configuration In NAT mode, the scope of the subnet is local to the IAP and forwards traffic through the IPSec tunnel or through the uplink. 1. Click New in the DHCP Server window and select Local to configure the following parameters for NAT mode DHCP pool. Name- Name of the subnet (must be unique). Type- Indicates the type of DHCP server. Available options are Local, Distributed L3, Distributed L2, Centralized L2. Local implies that this is a NAT mode DHCP subnet. Dell PowerConnect W-Series Instant Access Point 6.1.3.4-3.1.0.0 | User Guide VPN Configuration | 229