HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch Layer 3 - IP Services Configuration G - Page 129
IPv6 ND protocol, Address resolution
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 129 highlights
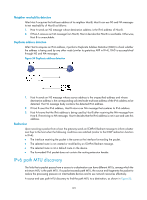
IPv6 ND protocol The IPv6 Neighbor Discovery (ND) protocol uses the following ICMPv6 messages: Table 8 ICMPv6 messages used by ND ICMPv6 message Type Neighbor Solicitation (NS) 135 Neighbor Advertisement (NA) 136 Router Solicitation (RS) 133 Router Advertisement (RA) 134 Redirect 137 Function Acquires the link-layer address of a neighbor. Verifies whether a neighbor is reachable. Detects duplicate addresses. Responds to an NS message. Notifies the neighboring nodes of link layer changes. Requests an address prefix and other configuration information for autoconfiguration after startup. Responds to an RS message. Advertises information, such as the Prefix Information options and flag bits. Informs the source host of a better next hop on the path to a particular destination when certain conditions are satisfied. Address resolution This function is similar to ARP in IPv4. An IPv6 node acquires the link-layer addresses of neighboring nodes on the same link through NS and NA messages. Figure 53 shows how Host A acquires the link-layer address of Host B on the same link. Figure 53 Address resolution The address resolution procedure is as follows: 1. Host A multicasts an NS message. The source address of the NS message is the IPv6 address of the sending interface of Host A and the destination address is the solicited-node multicast address of Host B. The NS message body contains the link-layer address of Host A and the target IPv6 address. 2. After receiving the NS message, Host B determines whether the target address of the packet is its IPv6 address. If yes, Host B learns the link-layer address of Host A, and then unicasts an NA message containing its link-layer address. 3. Host A acquires the link-layer address of Host B from the NA message. 121