HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch Layer 3 - IP Services Configuration G - Page 137
Configuring parameters for RA messages, Enabling sending of RA messages
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 137 highlights
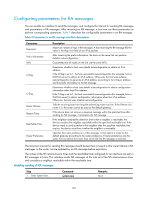
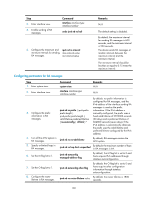
Configuring parameters for RA messages You can enable an interface to send RA messages, and configure the interval for sending RA messages and parameters in RA messages. After receiving an RA message, a host can use these parameters to perform corresponding operations. Table 9 describes the configurable parameters in an RA message. Table 9 Parameters in an RA message and their descriptions Parameter Hop Limit Prefix information MTU M flag O flag Router Lifetime Retrans Timer Reachable Time Router Preference Description Maximum number of hops in RA messages. A host receiving the RA message fills the value in the Hop Limit field of sent IPv6 packets. After receiving the prefix information, the hosts on the same link can perform stateless autoconfiguration. Guarantees that all nodes on the link use the same MTU. Determines whether a host uses stateful autoconfiguration to obtain an IPv6 address. If the M flag is set to 1, the host uses stateful autoconfiguration (for example, from a DHCPv6 server) to obtain an IPv6 address. Otherwise, the host uses stateless autoconfiguration to generate an IPv6 address according to its link-layer address and the prefix information in the RA message. Determines whether a host uses stateful autoconfiguration to obtain configuration information other than IPv6 address. If the O flag is set to 1, the host uses stateful autoconfiguration (for example, from a DHCPv6 server) to obtain configuration information other than IPv6 address. Otherwise, the host uses stateless autoconfiguration. Tells the receiving hosts how long the advertising router can live. If the lifetime of a router is 0, the router cannot be used as the default gateway. If the device does not receive a response message within the specified time after sending an NS message, it retransmits the NS message. If the neighbor reachability detection shows that a neighbor is reachable, the device considers the neighbor reachable within the specified reachable time. If the device needs to send a packet to the neighbor after the specified reachable time expires, the device reconfirms whether the neighbor is reachable. Specifies the router preference in a RA message. A host selects a router as the default gateway according to the router preference. If router preferences are the same, the host selects the router from which the first RA message is received. The maximum interval for sending RA messages should be less than (or equal to) the router lifetime in RA messages so the router can be updated by an RA message before expiration. The values of the NS retransmission timer and the reachable time configured for an interface are sent in RA messages to hosts. This interface sends NS messages at the interval of the NS retransmission timer and considers a neighbor reachable within the reachable time. Enabling sending of RA messages Step 1. Enter system view. Command system-view Remarks N/A 129