HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch Layer 3 - IP Services Configuration G - Page 178
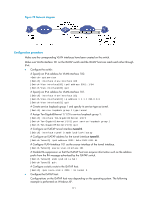
Configuring an ISATAP tunnel, Configuration example, Network requirements
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 178 highlights
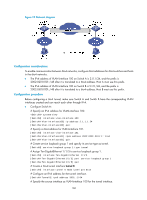
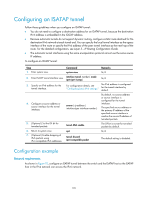
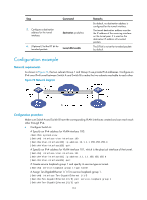
Configuring an ISATAP tunnel Follow these guidelines when you configure an ISATAP tunnel: • You do not need to configure a destination address for an ISATAP tunnel, because the destination IPv4 address is embedded in the ISATAP address. • Because automatic tunnels do not support dynamic routing, configure a static route destined for the destination IPv6 network at each tunnel end. You can specify the local tunnel interface as the egress interface of the route or specify the IPv6 address of the peer tunnel interface as the next hop of the route. For the detailed configuration, see Layer 3-IP Routing Configuration Guide. • The automatic tunnel interfaces using the same encapsulation protocol cannot use the same source IP address. To configure an ISATAP tunnel: Step Command Remarks 1. Enter system view. system-view N/A 2. Enter ISATAP tunnel interface view. interface tunnel number [ mode ipv6-ipv4 isatap ] N/A 3. Specify an IPv6 address for the tunnel interface. For configuration details, see "Configuring basic IPv6 settings." No IPv6 address is configured for the tunnel interface by default. 4. Configure a source address or source interface for the tunnel interface. source { ip-address | interface-type interface-number } By default, no source address or source interface is configured for the tunnel interface. The specified source address or the primary IP address of the specified source interface is used as the source IP address of tunneled packets. 5. (Optional.) Set the DF bit for tunneled packets. tunnel dfbit enable The DF bit is not set for tunneled packets by default. 6. Return to system view. quit N/A 7. (Optional.) Enable dropping of IPv6 packets using IPv4-compatible IPv6 addresses. tunnel discard ipv4-compatible-packet The default setting is disabled. Configuration example Network requirements As shown in Figure 75, configure an ISATAP tunnel between the switch and the ISATAP host so the ISATAP host in the IPv4 network can access the IPv6 network. 170