HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch Layer 3 - IP Services Configuration G - Page 130
Neighbor reachability detection, Duplicate address detection, Redirection, IPv6 path MTU discovery
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 130 highlights
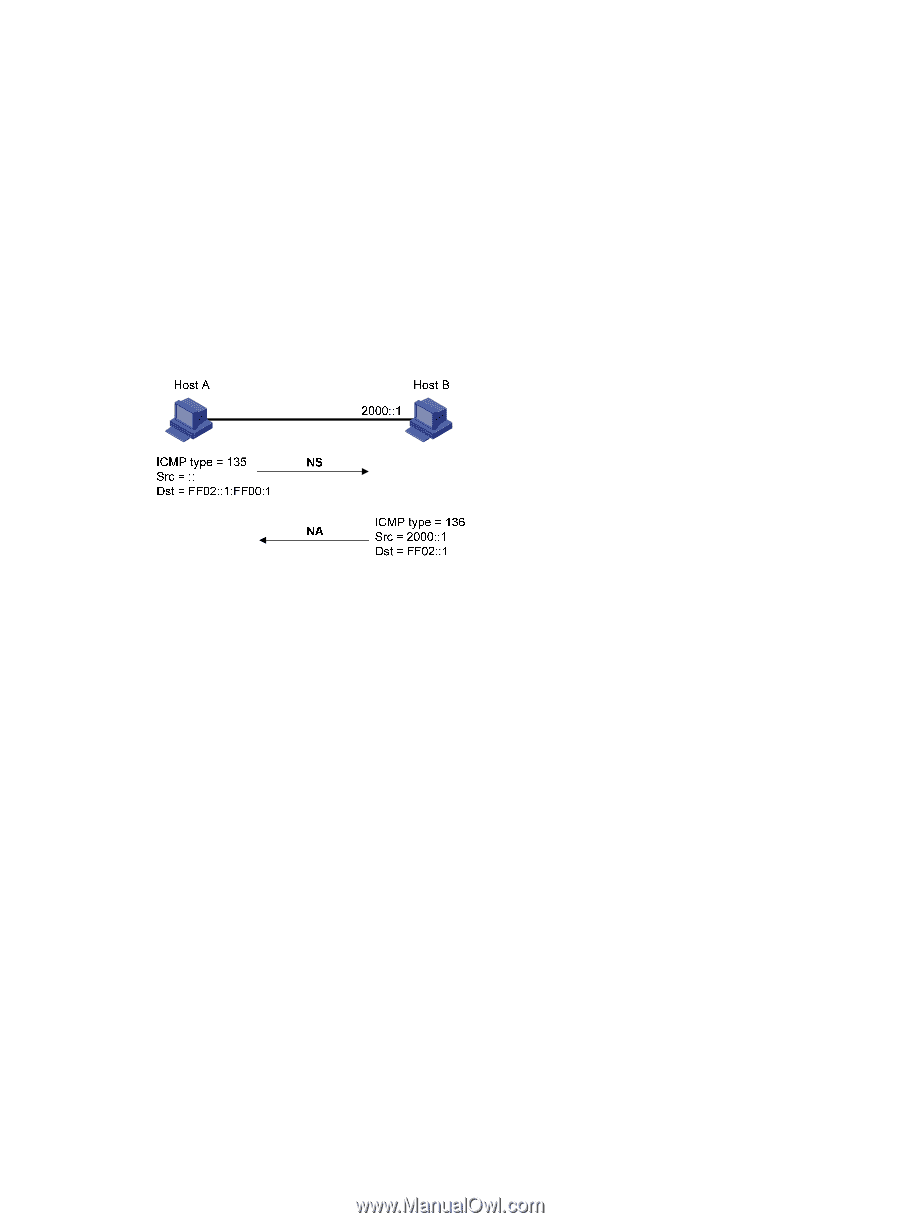
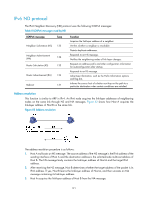
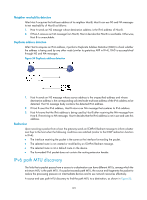
Neighbor reachability detection After Host A acquires the link-layer address of its neighbor Host B, Host A can use NS and NA messages to test reachability of Host B as follows: 1. Host A sends an NS message whose destination address is the IPv6 address of Host B. 2. If Host A receives an NA message from Host B, Host A decides that Host B is reachable. Otherwise, Host B is unreachable. Duplicate address detection After Host A acquires an IPv6 address, it performs Duplicate Address Detection (DAD) to check whether the address is being used by any other node (similar to gratuitous ARP in IPv4). DAD is accomplished through NS and NA messages. Figure 54 Duplicate address detection 1. Host A sends an NS message whose source address is the unspecified address and whose destination address is the corresponding solicited-node multicast address of the IPv6 address to be detected. The NS message body contains the detected IPv6 address. 2. If Host B uses this IPv6 address, Host B returns an NA message that contains its IPv6 address. 3. Host A knows that the IPv6 address is being used by Host B after receiving the NA message from Host B. If receiving no NA message, Host A decides that the IPv6 address is not in use and uses this address. Redirection Upon receiving a packet from a host, the gateway sends an ICMPv6 Redirect message to inform a better next hop to the host when the following conditions are satisfied (similar to the ICMP redirection function in IPv4): • The interface receiving the packet is the same as the interface forwarding the packet. • The selected route is not created or modified by an ICMPv6 Redirect message. • The selected route is not a default route on the device. • The forwarded IPv6 packet does not contain the routing extension header. IPv6 path MTU discovery The links that a packet passes from a source to a destination can have different MTUs, among which the minimum MTU is the path MTU. If a packet exceeds path MTU, the source end fragments the packet to reduce the processing pressure on intermediate devices and to use network resources effectively. A source end uses path MTU discovery to find the path MTU to a destination, as shown in Figure 55. 122