HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch Layer 3 - IP Services Configuration G - Page 53
DHCP server configuration examples, Static IP address assignment configuration example
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 53 highlights
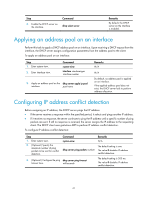
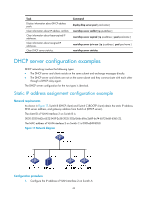
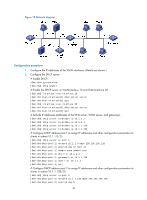
Task Display information about DHCP address pools. Clear information about IP address conflicts. Clear information about lease-expired IP addresses. Clear information about assigned IP addresses. Clear DHCP server statistics. Command display dhcp server pool [ pool-name ] reset dhcp server conflict [ ip ip-address ] reset dhcp server expired [ ip ip-address | pool pool-name ] reset dhcp server ip-in-use [ ip ip-address | pool pool-name ] reset dhcp server statistics DHCP server configuration examples DHCP networking involves the following types: • The DHCP server and clients reside on the same subnet and exchange messages directly. • The DHCP server and clients are not on the same subnet and they communicate with each other through a DHCP relay agent. The DHCP server configuration for the two types is identical. Static IP address assignment configuration example Network requirements As shown in Figure 17, Switch B (DHCP client) and Switch C (BOOTP client) obtain the static IP address, DNS server address, and gateway address from Switch A (DHCP server). The client ID of VLAN-interface 2 on Switch B is: 0030-3030-662e-6532-3439-2e38-3035-302d-566c-616e-2d69-6e74-6572-6661-6365-32. The MAC address of VLAN-interface 2 on Switch C is 000f-e249-8050. Figure 17 Network diagram Configuration procedure 1. Configure the IP address of VLAN-interface 2 on Switch A: 44