HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch Layer 3 - IP Services Configuration G - Page 42
Specifying a primary subnet and multiple secondary subnets for a DHCP address pool, Command, Remarks
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 42 highlights
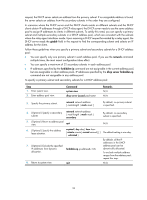
Step 1. Enter system view. Command system-view Remarks N/A 2. Create a DHCP user class and enter DHCP user class view. dhcp class class-name Required for client classification. By default, no DHCP user class exists. Required for client 3. Configure the match rule for the if-match option option-code [ hex classification. DHCP user class. hex-string [ offset offset length length By default, no match rule is | mask mask ] ] specified for a DHCP user class. 4. Return to system view. quit N/A 5. Enter address pool view. dhcp server ip-pool pool-name N/A 6. Specify the primary subnet for the address pool. network network-address [ mask-length | mask mask ] By default, no primary subnet is specified. 7. (Optional.) Specify the common address range start-ip-address address range. end-ip-address By default, no IP address range is specified. 8. (Optional.) Specify an IP address range for a DHCP user class class-name range class. start-ip-address end-ip-address By default, no IP address range is specified for a user class. The DHCP user class must already exist. To specify address ranges for multiple DHCP user classes, repeat this step. 9. (Optional.) Specify the address expired { day day [ hour hour lease duration. [ minute minute [ second second ] ] ] The default setting is one day. | unlimited } 10. (Optional.) Exclude the specified IP addresses in the address pool from dynamic allocation. forbidden-ip ip-address& By default, all the IP addresses in the DHCP address pool are assignable. To exclude multiple address ranges from dynamic allocation, repeat this step. 11. Return to system view. quit N/A 12. (Optional.) Exclude the specified IP addresses from automatic allocation globally. dhcp server forbidden-ip start-ip-address [ end-ip-address ] By default, except for the IP address of the DHCP server interface, all IP addresses in address pools are assignable. To exclude multiple IP address ranges, repeat this step. Specifying a primary subnet and multiple secondary subnets for a DHCP address pool In scenarios where the DHCP server and the DHCP clients reside on the same subnet, the DHCP server needs to assign addresses in different address ranges to the DHCP clients. To satisfy this need, you can specify a primary subnet and multiple secondary subnets in an address pool. Upon receiving a client 33