HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch Layer 3 - IP Services Configuration G - Page 192
Configuring GRE, Overview, GRE encapsulation format
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 192 highlights
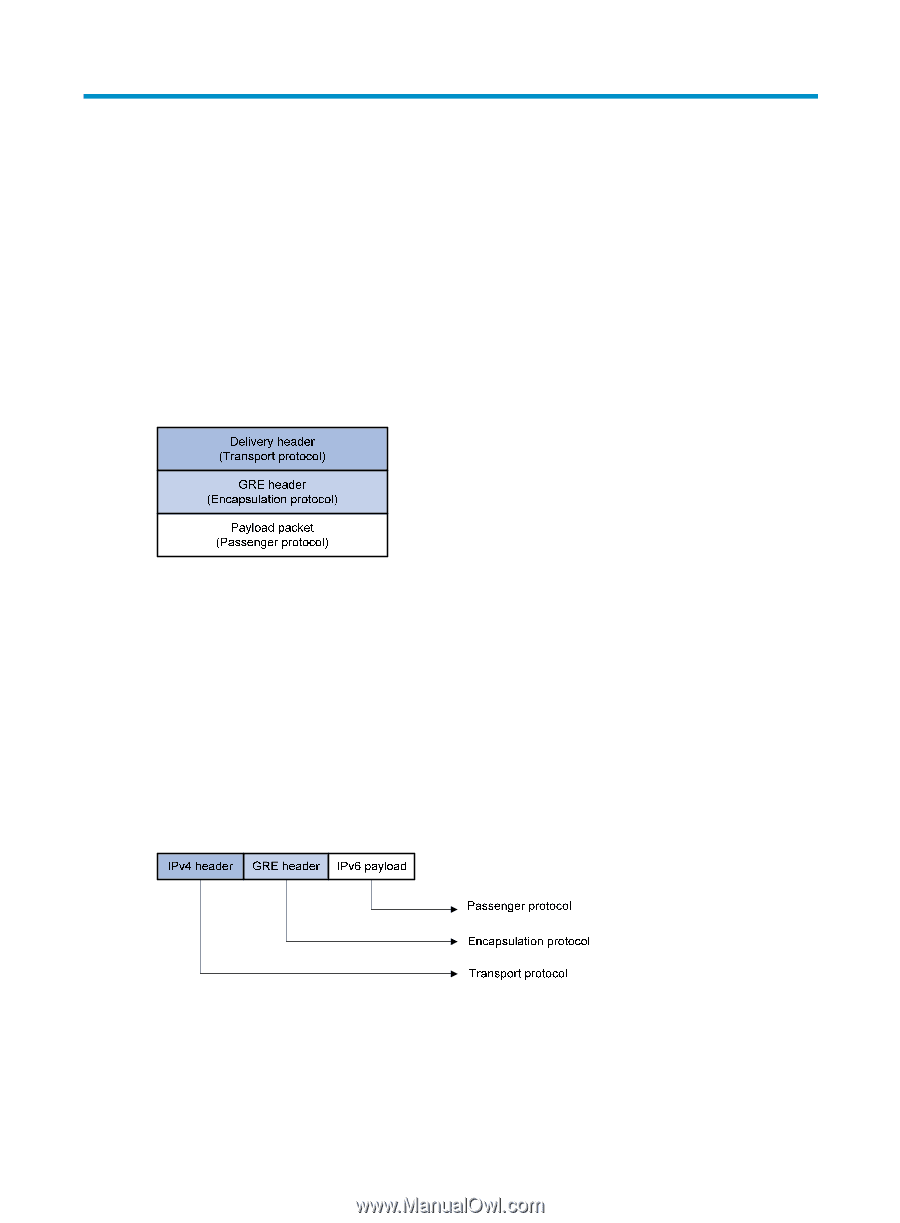
Configuring GRE Overview Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) is a tunneling protocol that can encapsulate multiple network layer protocols into virtual point-to-point tunnels over an IP network. Packets are encapsulated at one tunnel end and de-encapsulated at the other tunnel end. GRE encapsulation format Figure 79 GRE encapsulation format As shown in Figure 79, a GRE-tunneled packet comprises the following parts: • Payload packet-Original packet. The protocol type of the payload packet is called the passenger protocol. • GRE header-After GRE receives a payload packet, it adds a GRE header to the payload packet to change the payload packet to a GRE packet. GRE is called the encapsulation protocol. • Delivery header-Transport protocol used to transfer the GRE packet. The system adds a transport protocol header to the GRE packet to deliver it to the tunnel end. For example, to transfer an IPv6 packet over an IPv4 network through a GRE tunnel, the system encapsulates the IPv6 packet in the format shown in Figure 80. The passenger protocol is IPv6, the encapsulation protocol is GRE, and the transport protocol is IPv4. Figure 80 Format of a GRE-encapsulated packet Depending on the transport protocol, GRE tunnels fall into the following types: • GRE over IPv4-The transport protocol is IPv4, and the passenger protocol is any network layer protocol. • GRE over IPv6-The transport protocol is IPv6, and the passenger protocol is any network layer protocol. 184