HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch Layer 3 - IP Services Configuration G - Page 99
IPv6 DNS configuration examples, Static domain name resolution configuration example, Network
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
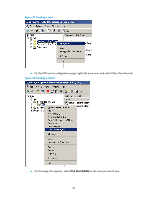
Page 99 highlights
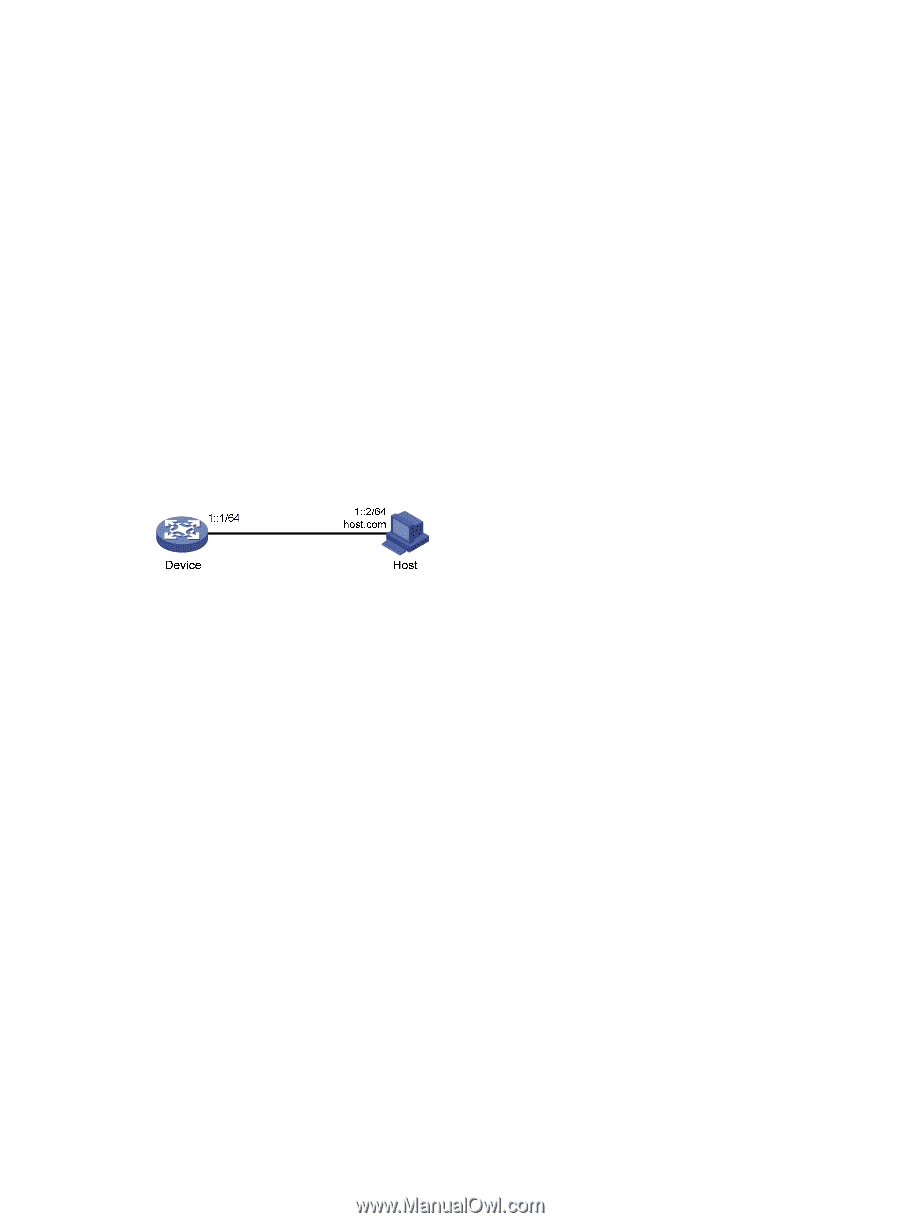
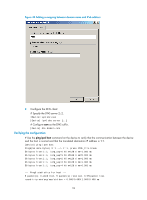
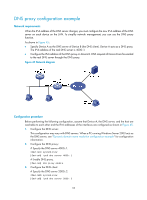
56 bytes from 3.1.1.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=255 time=1.000 ms 56 bytes from 3.1.1.1: icmp_seq=3 ttl=255 time=1.000 ms 56 bytes from 3.1.1.1: icmp_seq=4 ttl=255 time=2.000 ms --- Ping statistics for host.com --5 packet(s) transmitted, 5 packet(s) received, 0.0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max/std-dev = 1.000/1.200/2.000/0.400 ms IPv6 DNS configuration examples Static domain name resolution configuration example Network requirements As shown in Figure 39, the device wants to access the host by using an easy-to-remember domain name rather than an IPv6 address. Configure static domain name resolution on the device so that the device can use the domain name host.com to access the host whose IPv6 address is 1::2. Figure 39 Network diagram Configuration procedure # Configure a mapping between host name host.com and IPv6 address 1::2. system-view [Device] ipv6 host host.com 1::2 # Use the ping ipv6 host.com command to verify that the device can use static domain name resolution to resolve domain name host.com into IPv6 address 1::2. [Sysname] ping ipv6 host.com Ping6(56 data bytes) 1::1 --> 1::2, press CTRL_C to break 56 bytes from 1::2, icmp_seq=0 hlim=128 time=1.000 ms 56 bytes from 1::2, icmp_seq=1 hlim=128 time=0.000 ms 56 bytes from 1::2, icmp_seq=2 hlim=128 time=1.000 ms 56 bytes from 1::2, icmp_seq=3 hlim=128 time=1.000 ms 56 bytes from 1::2, icmp_seq=4 hlim=128 time=0.000 ms --- Ping6 statistics for host.com --5 packet(s) transmitted, 5 packet(s) received, 0.0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max/std-dev = 0.000/0.600/1.000/0.490 ms 90