HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch Layer 3 - IP Services Configuration G - Page 89
Configuring the IPv4 DNS client, Configuring static domain name resolution, Configuration guidelines
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 89 highlights
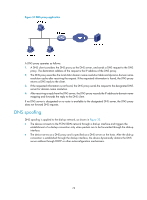
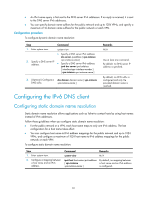
Tasks at a glance (Optional.) Configuring the DNS trusted interface Configuring the IPv4 DNS client Configuring static domain name resolution Static domain name resolution allows applications such as Telnet to contact hosts by using host names instead of IPv4 addresses. Follow these guidelines when you configure static domain name resolution: • On the public network or a VPN, each host name maps to only one IPv4 address. The most recent configuration for a host name takes effect. • You can configure host name-to-IPv4 address mappings for the public network and up to 1024 VPNs, and configure a maximum of 1024 host name-to-IPv4 address mappings for the public network or each VPN. To configure static domain name resolution: Step 1. Enter system view. 2. Configure a mapping between a host name and an IPv4 address. Command system-view ip host host-name ip-address [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] Remarks N/A By default, no mapping between a host name and an IPv4 address is configured. Configuring dynamic domain name resolution To use dynamic domain name resolution, configure DNS servers so that DNS queries can be sent to a correct server for resolution. A DNS server manually configured takes precedence over the one dynamically obtained through DHCP, and a DNS server configured earlier takes precedence. A name query is first sent to the DNS server that has the highest priority. If no reply is received, it is sent to the DNS server that has the second highest priority, and thus in turn. In addition, you can configure a DNS suffix that the system automatically adds to the provided domain name for resolution. A DNS suffix manually configured takes precedence over the one dynamically obtained through DHCP, and a DNS suffix configured earlier takes precedence. The DNS resolver first uses the suffix that has the highest priority. If the name resolution fails, the DNS resolver uses the suffix that has the second highest priority, and thus in turn. Configuration guidelines Follow these guidelines when you configure dynamic domain name resolution: • You can specify DNS server IPv4 addresses for the public network and up to 1024 VPNs, and specify a maximum of six DNS server IPv4 addresses for the public network or each VPN. • You can specify DNS server IPv6 addresses for the public network and up to 1024 VPNs, and specify a maximum of six DNS server IPv6 addresses for the public network or each VPN. 80