HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch Layer 3 - IP Services Configuration G - Page 98
Configuration procedure, Verifying the configuration, Enable DNS proxy.
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 98 highlights
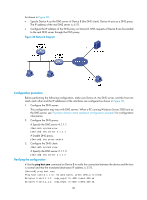
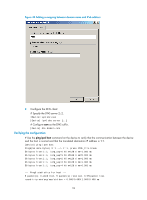
As shown in Figure 38: • Specify Device A as the DNS server of Device B (the DNS client). Device A acts as a DNS proxy. The IP address of the real DNS server is 4.1.1.1. • Configure the IP address of the DNS proxy on Device B. DNS requests of Device B are forwarded to the real DNS server through the DNS proxy. Figure 38 Network diagram Configuration procedure Before performing the following configuration, make sure Device A, the DNS server, and the host can reach each other and the IP addresses of the interfaces are configured as shown in Figure 38. 1. Configure the DNS server: This configuration may vary with DNS servers. When a PC running Windows Server 2000 acts as the DNS server, see "Dynamic domain name resolution configuration example" for configuration information. 2. Configure the DNS proxy: # Specify the DNS server 4.1.1.1. system-view [DeviceA] dns server 4.1.1.1 # Enable DNS proxy. [DeviceA] dns proxy enable 3. Configure the DNS client: system-view # Specify the DNS server 2.1.1.2. [DeviceB] dns server 2.1.1.2 Verifying the configuration # Use the ping host.com command on Device B to verify the connection between the device and the host is normal and that the translated destination IP address is 3.1.1.1. [DeviceB] ping host.com Ping host.com (3.1.1.1): 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break 56 bytes from 3.1.1.1: icmp_seq=0 ttl=255 time=1.000 ms 56 bytes from 3.1.1.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=255 time=1.000 ms 89