HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch Layer 3 - IP Services Configuration G - Page 170
Protocols and standards, Tunneling configuration task list, Configuring a tunnel interface
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 170 highlights
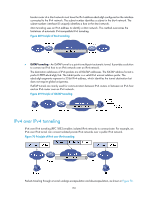
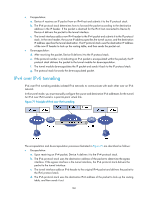
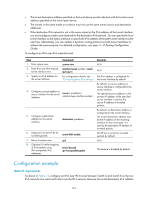
Protocols and standards • RFC 1853, IP in IP Tunneling • RFC 2473, Generic Packet Tunneling in IPv6 Specification • RFC 2893, Transition Mechanisms for IPv6 Hosts and Routers • RFC 3056, Connection of IPv6 Domains via IPv4 Clouds • RFC 4214, Intra-Site Automatic Tunnel Addressing Protocol (ISATAP) Tunneling configuration task list Tasks at a glance (Required.) Configuring a tunnel interface Perform one of the following tasks: • Configuring an IPv6 over IPv4 tunnel: { Configuring an IPv6 over IPv4 manual tunnel { Configuring a 6to4 tunnel { Configuring an ISATAP tunnel • Configuring an IPv4 over IPv4 tunnel • Configuring an IPv4 over IPv6 tunnel • Configuring an IPv6 over IPv6 tunnel Configuring a tunnel interface Configure a Layer 3 virtual tunnel interface on each device on a tunnel so that devices at both ends can send, identify, and process packets from the tunnel. A tunneled packet cannot be directly routed based on its destination address. The packet should be sent to a tunnel-type service loopback group, which then delivers the packet to the forwarding module for Layer 3 forwarding. Therefore, you must configure a tunnel-type service loopback group. Otherwise, the tunnel interface will fail to forward and receive packets. For information about service loopback group, see Layer 2-LAN Switching Configuration Guide. To configure a tunnel interface: Step 1. Enter system view. Command system-view Remarks N/A 162