HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch Layer 3 - IP Services Configuration G - Page 151
Stateless DHCPv6, Protocols and standards
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 151 highlights
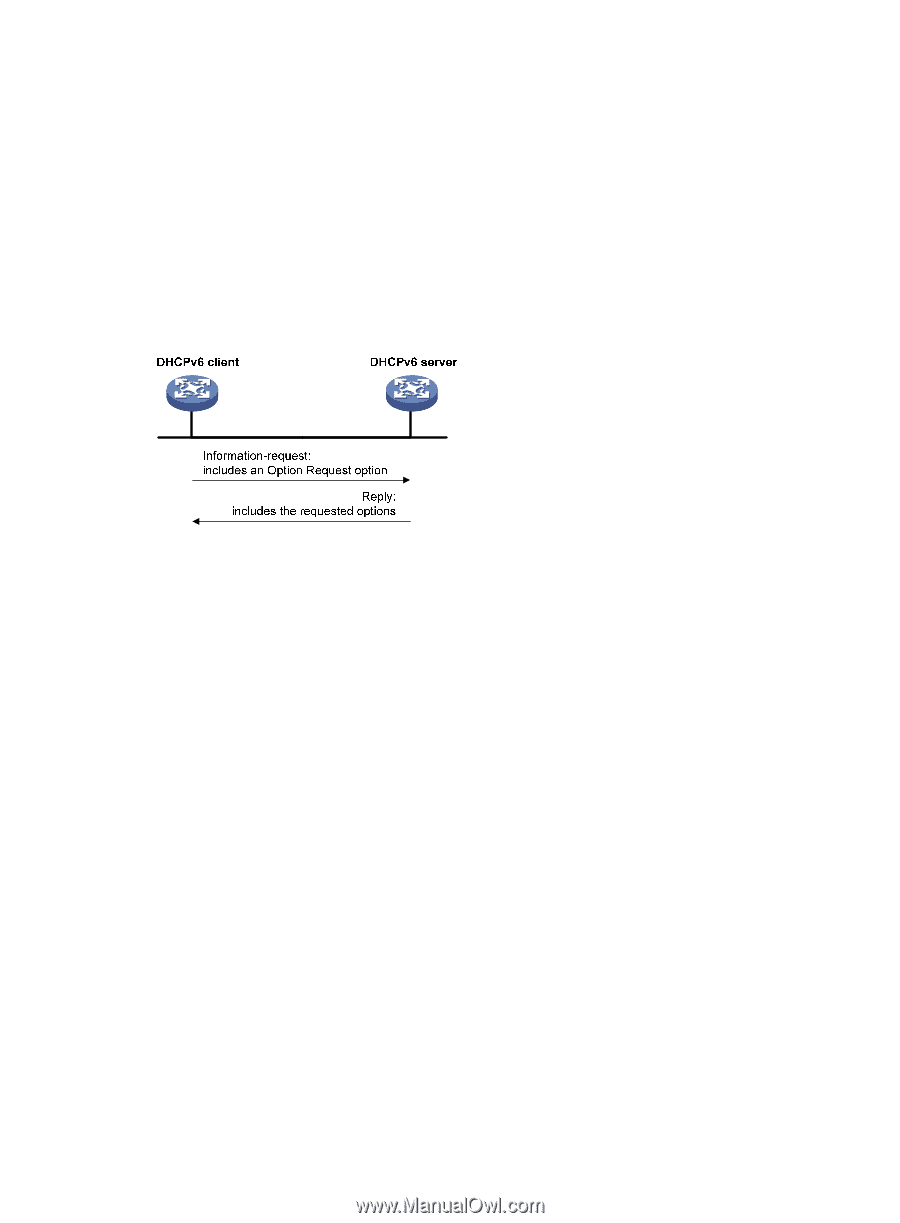
Stateless DHCPv6 Stateless DHCPv6 enables a device that has obtained an IPv6 address/prefix to get other configuration parameters from a DHCPv6 server. The device decides whether to perform stateless DHCP according to the managed address configuration flag (M flag) and the other stateful configuration flag (O flag) in the RA message received from the router during stateless address autoconfiguration. If the M flag is set to 0 and the O flag is set to 1, the device performs stateless DHCP to get other configuration parameters. For more information about stateless address autoconfiguration, see "Configuring basic IPv6 settings." Figure 61 Stateless DHCPv6 operation As shown in Figure 61, stateless DHCPv6 operates in the following steps: 1. The DHCPv6 client sends an Information-request message to the multicast address of all DHCPv6 servers and DHCPv6 relay agents. The Information-request message contains an Option Request option that specifies the requested configuration parameters. 2. The DHCPv6 server returns to the client a Reply message containing the requested configuration parameters. 3. The client checks the Reply message. If the obtained configuration parameters match those requested in the Information-request message, the client uses these parameters to complete configuration. If not, the client ignores the configuration parameters. If the client receives multiple replies, it uses the first received reply. Protocols and standards • RFC 3736, Stateless Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Service for IPv6 • RFC 3315, Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6 (DHCPv6) • RFC 2462, IPv6 Stateless Address Autoconfiguration • RFC 3633, IPv6 Prefix Options for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) version 6 143