Dell PowerEdge XE2420 EMC Installation and Service Manual - Page 103
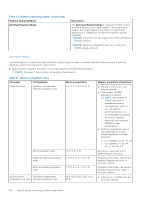
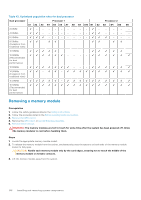
Mode-specific guidelines, Table 40. Memory operating modes
 |
View all Dell PowerEdge XE2420 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 103 highlights
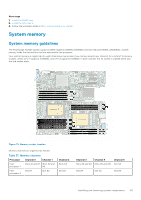
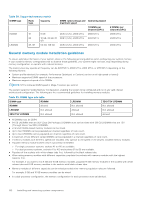
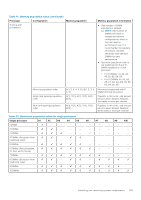
For example, if you populate socket A1 for processor 1, then populate socket B1 for processor 2, and so on. ● Mixing of more than two memory module capacities in a system is not supported. ● Unbalanced memory configurations result in a performance loss so always populate memory channels identically with identical DIMMs for best performance. ● Populate six identical memory modules per processor (one DIMM per channel) at a time to maximize performance. Mode-specific guidelines The configurations allowed depend on the memory mode selected in the System BIOS. Table 40. Memory operating modes Memory Operating Mode Optimizer Mode Description The Optimizer Mode if enabled, the DRAM controllers operate independently in the 64-bit mode and provide optimized memory performance. Mirror Mode Single Rank Spare Mode Multi Rank Spare Mode The Mirror Mode if enabled, the system maintains two identical copies of data in memory, and the total available system memory is one half of the total installed physical memory. Half of the installed memory is used to mirror the active memory modules. This feature provides maximum reliability and enables the system to continue running even during a catastrophic memory failure by switching over to the mirrored copy. The installation guidelines to enable Mirror Mode require that the memory modules be identical in size, speed, and technology, and they must be populated in sets of 6 per processor. Single Rank Spare Mode allocates one rank per channel as a spare. If excessive correctable errors occur in a rank or channel, while the operating system is running, they are moved to the spare area to prevent errors from causing an uncorrectable failure. Requires two or more ranks to be populated in each channel. Multi Rank Spare Mode allocates two ranks per channel as a spare. If excessive correctable errors occur in a rank or channel, while the operating system is running, they are moved to the spare area to prevent errors from causing an uncorrectable failure. Requires three or more ranks to be populated in each channel. With single rank memory sparing enabled, the system memory available to the operating system is reduced by one rank per channel. For example, in a dual-processor configuration with sixteen 16 GB dual-rank memory modules, the available system memory: 16 GB x 16(memory modules) - 8GB(1 rank sparing/channel) x 12(channel) = 256 GB - 96 GB = 160 GB For multi rank sparing, in a dual-processor configuration with sixteen 64 GB quad-rank memory modules, the available system memory: 64 GB x 16(memory modules) - 32 GB(2 rank sparing/channel) x 12 (channel) = 1024 GB - 384 GB = 640 GB NOTE: To use memory sparing, this feature must be enabled in the BIOS menu of System Setup. NOTE: Memory sparing does not offer protection against a multi-bit uncorrectable error. Installing and removing system components 103