Netgear FS752TPS FS752TS Setup Manual - Page 104
Fast Link, Port State, Speed, Path Cost, Priority, STP Status, APPLY
 |
View all Netgear FS752TPS manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 104 highlights
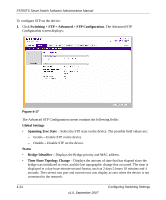
FS700TS Smart Switch Software Administration Manual • Fast Link - Select the Fast Link state on the interface. If Fast Link mode is enabled for a interface, the Port State is automatically placed in the Forwarding state when the port link is up. Fast Link optimizes the STP protocol convergence. The possible field values are: - Enable - Enable Fast Link on the interface. - Disable - Disable Fast Link on the interface. • Port State - Displays the current STP state of a port. If enabled, the port state determines what forwarding action is taken on traffic. Possible port states are: - Forwarding - STP is enabled on the port, and the port is forwarding packets based on the STP topology. - Disabled - STP is currently disabled on the port. The port forwards traffic while learning MAC addresses. - Blocking - The port is currently blocked and cannot forward traffic or learn MAC addresses. Blocking is displayed when STP is enabled. - Listening - The port is in Listening mode. The port cannot forward traffic nor can it learn MAC addresses. - Learning - The port is in Learning mode. The port cannot forward traffic, however it can learn new MAC addresses. • Speed - Displays the speed at which the port is operating. • Path Cost - Enter the method used to assign default path cost to STP ports. The possible field range is 1 - 200000000. The default path cost assigned to an interface varies according to the selected method. • Priority - Enter the port priority value. When switches or ports are running STP, each is assigned a priority. After exchanging BPDUs, the device with the lowest priority value becomes the Root Port. The default value is 32768. The port priority value is provided in increments of 4096. 2. Select the STP Status and Fast Link status in the provided fields. 3. Enter the Path Cost and Priority in the provided fields. 4. Click APPLY to update the device. 4-28 v1.0, September 2007 Configuring Switching Settings