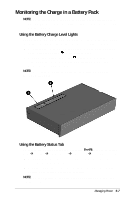
Compaq Armada E700 Compaq Armada E700 Series Reference Guide - Page 47
Setting Power Preferences
 |
View all Compaq Armada E700 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 47 highlights
Setting Power Preferences You can increase, decrease, and allocate the power used by the computer by setting power preferences. s Increasing power increases performance, while decreasing power conserves energy and extends battery operating time. s By decreasing power to unused components and functions, you can allocate more power to the components and functions you are currently using. Many power preferences are timeout settings. s A timeout is the period of inactivity before the system initiates a power change or reduces power to a component. For example, the computer is preset to initiate Suspend (Standby) after a period of inactivity. The time interval between when you stop using the computer and the onset of system-initiated Suspend (Standby) is a Suspend (Standby) timeout s Depending on your operating system, you can set timeouts that are specific to various conditions, components, or procedures as well as specify the duration of those timeouts. The following tables list power preference procedures that are not described in your operating system documentation. s For additional power preference options, refer to your operating system documentation. s For a summary of power preference settings that extend battery operating time, refer to "Conserving Battery Power" later in this chapter. 5-12 Managing Power