HP StorageWorks MSA 2/8 HP StorageWorks Fabric OS Procedures V3.1.x/4.1.x User - Page 145
Recommendations, New Fabrics, Existing Fabrics
 |
View all HP StorageWorks MSA 2/8 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 145 highlights
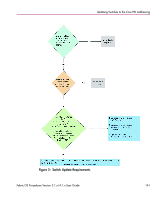
Updating Switches to the Core PID Addressing Recommendations Redundant fabrics and multi-pathing software are recommended for uptime-sensitive environments. If redundant fabrics are not used, there are numerous possible failure cases and even routine maintenance scenarios that can result in application downtime. This is true for any currently available Fibre Channel technology. Examples of scenarios protected by redundant fabrics include: ■ Add/move/change operations for devices or switches ■ Major upgrades/changes to fabric architecture ■ Physical disasters ■ Changing the Core PID format ■ Changing any other fabric-wide parameters, for example ED_TOV ■ Erroneous zoning changes/user error New Fabrics For new fabrics, the PID format should always be set to the larger port count addressing method before the fabric enters production. When updating an existing SAN, there are several scenarios which must be evaluated before changing the PID format. Proactively setting the core PID format on new fabrics is strongly recommended to save potential administrative effort later on. There is no difference in the behavior of a fabric with either PID format. Core PID is enabled by default on 4.x switches (Core Switch 2/64 or SAN Switch 2/32). Use the configure command to enable Core PID on 2.x and 3.x switches before mixing with a 4.x switch fabric. Existing Fabrics When a switch with the larger port count format is introduced into an existing fabric, the core PID format must be set on all switches in the fabric to prevent segmentation. This does not require application downtime if redundant fabrics are used. If redundant fabrics are not in use, it is necessary to schedule an outage for the fabric. Fabric OS Procedures Version 3.1.x/4.1.x User Guide 145