Symantec 14541094 User Guide - Page 23
About connecting over the Internet, About cable modem connections, About DSL or ADSL connections
 |
UPC - 037648640480
View all Symantec 14541094 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 23 highlights
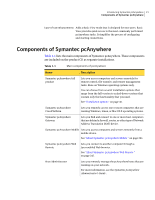
Introducing Symantec pcAnywhere 23 How Symantec pcAnywhere works the host computer, anything that happens on the host computer screen is also displayed on the remote computer screen. See "Ways to set up a remote computer" on page 92. About connecting over the Internet Symantec pcAnywhere lets you connect to a host computer over the Internet, provided that both the host and the remote computers have Internet access. If the host computer has a public IP address, connecting over the Internet involves the following process: ■ The host user connects to the Internet, following the instructions provided by the Internet service provider (ISP). ■ In pcAnywhere, the host user starts a host session that is configured for TCP/IP. See "Ways to start a host session" on page 84. ■ The remote user connects to the Internet, following the instructions provided by the ISP. ■ In pcAnywhere, the remote user configures a TCP/IP connection, specifying the IP address of the host computer and the logon information. See "Configuring a remote network connection" on page 96. ■ The remote user starts the pcAnywhere remote connection item. See "Ways to start a remote control session" on page 109. About cable modem connections Unlike traditional modems, which convert analog and digital signals to exchange data over a telephone line, cable modems use Internet protocols to transmit data over a cable television line. Because cable modems use TCP/IP to transmit data, cable modem connections must be configured as TCP/IP network connections. The default Network, Cable, DSL connection item in pcAnywhere is configured for TCP/IP. See "Configuring a host network connection" on page 75. See "Configuring a remote network connection" on page 96. About DSL or ADSL connections Digital subscriber lines, such as ADSL or DSL, are high-speed Internet connections offered by an Internet service provider (ISP). Your computer operates as though it is connected to a network and is assigned an IP address. DSL and ADSL connections must be configured as TCP/IP network connections.